지원
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS 지원.
초록
1장. 지원 개요
Red Hat은 클러스터, 모니터링 및 문제 해결을 위한 클러스터 관리자 툴을 제공합니다.
1.1. 지원 받기
지원 받기: Red Hat 고객 포털을 방문하여 지식 베이스 문서를 검토하고, 지원 케이스를 제출하고, 추가 제품 설명서 및 리소스를 검토하십시오.
1.2. HO원격 상태 모니터링 문제
원격 상태 모니터링 문제: AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 클러스터에 대한 Telemetry 및 구성 데이터를 수집하고 Telemeter Client 및 Insights Operator를 사용하여 Red Hat에 보고합니다. Red Hat은 이 데이터를 사용하여 연결된 클러스터 의 문제를 이해하고 해결합니다. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS는 다음을 사용하여 데이터 및 상태를 모니터링합니다.
Telemetry: Telemetry 클라이언트는 4분 30초마다 지표 값을 수집하여 Red Hat에 업로드합니다. Red Hat은 이 데이터를 사용하여 다음을 수행합니다.
- 클러스터를 모니터링합니다.
- AWS 업그레이드 시 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 롤아웃합니다.
- 업그레이드 환경을 개선합니다.
Insights Operator: 기본적으로 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 2시간마다 구성 및 구성 요소 실패 상태를 보고하는 Cryostat Operator를 설치하고 활성화합니다. DestinationRule Operator는 다음을 수행하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
- 잠재적인 클러스터 문제를 사전에 파악합니다.
- Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager에서 솔루션 및 예방 조치를 제공합니다.
Telemetry 정보를 검토 할 수 있습니다.
원격 상태 보고를 활성화한 경우 Insights를 사용하여 문제를 식별합니다. 선택적으로 원격 상태 보고를 비활성화할 수 있습니다.
1.3. 문제 해결
클러스터 관리자는 AWS 구성 요소 문제에서 다음 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 모니터링하고 해결할 수 있습니다.
노드 문제: 클러스터 관리자는 노드의 상태, 리소스 사용량 및 구성을 검토하여 노드 관련 문제를 확인하고 해결할 수 있습니다. 다음을 쿼리할 수 있습니다.
- 노드의 kubelet 상태입니다.
- 클러스터 노드 저널 로그입니다.
Operator 문제: 클러스터 관리자는 다음을 수행하여 Operator 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- Operator 서브스크립션 상태를 확인합니다.
- Operator Pod 상태를 확인합니다.
- Operator 로그를 수집합니다.
Pod 문제: 클러스터 관리자는 Pod 상태를 검토하고 다음을 완료하여 Pod 관련 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- Pod 및 컨테이너 로그를 검토합니다.
- root 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
스토리지 문제: 실패한 노드가 연결된 볼륨을 마운트 해제할 수 없기 때문에 새 노드의 마운트 볼륨이 불가능한 경우 다중 연결 스토리지 오류가 발생합니다. 클러스터 관리자는 다음을 수행하여 다중 연결 스토리지 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- RWX 볼륨을 사용하여 여러 연결을 활성화합니다.
- RWO 볼륨을 사용할 때 오류가 발생한 노드를 복구하거나 삭제합니다.
모니터링 문제: 클러스터 관리자는 모니터링을 위해 문제 해결 페이지의 절차를 따를 수 있습니다. 사용자 정의 프로젝트의 지표를 사용할 수 없거나 Prometheus가 많은 디스크 공간을 사용하는 경우 다음을 확인하십시오.
- 사용자 정의 메트릭을 사용할 수 없는 이유를 조사합니다.
- Prometheus가 많은 디스크 공간을 소비하는 이유를 확인합니다.
로깅 문제: 클러스터 관리자는 "지원" 및 "Troubleshooting logging" 섹션의 절차를 따라 로깅 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc) 문제: 로그 수준을 늘려 OpenShift CLI(oc) 문제 조사
2장. 클러스터 리소스 관리
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 글로벌 구성 옵션을 적용할 수 있습니다. Operator는 이러한 구성 설정을 클러스터 전체에 적용합니다.
2.1. 클러스터 리소스와 상호 작용
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 OpenShift CLI(oc) 툴을 사용하여 클러스터 리소스와 상호 작용할 수 있습니다. oc api-resources 명령을 실행한 후 표시되는 클러스터 리소스를 편집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
웹 콘솔에 액세스하거나
ocCLI 툴을 설치했습니다.
프로세스
적용된 구성 Operator를 보려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ oc api-resources -o name | grep config.openshift.io
구성할 수 있는 클러스터 리소스를 보려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ oc explain <resource_name>.config.openshift.io
클러스터에서 CRD(사용자 정의 리소스 정의) 오브젝트의 구성을 보려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ oc get <resource_name>.config -o yaml
클러스터 리소스 구성을 편집하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ oc edit <resource_name>.config -o yaml
3장. 지원 요청
3.1. 지원 요청
이 문서에 설명된 절차 또는 일반적으로 Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS에 문제가 발생하는 경우 Red Hat 고객 포털 을 방문하십시오.
고객 포털에서 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- Red Hat 제품과 관련된 기사 및 솔루션에 대한 Red Hat 지식베이스를 검색하거나 살펴볼 수 있습니다.
- Red Hat 지원에 대한 지원 케이스 제출할 수 있습니다.
- 다른 제품 설명서에 액세스 가능합니다.
클러스터 문제를 식별하기 위해 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 Insights를 사용할 수 있습니다. Insights는 문제에 대한 세부 정보 및 문제 해결 방법에 대한 정보를 제공합니다.
이 문서를 개선하기 위한 제안이 있거나 오류를 발견한 경우 가장 관련 문서 구성 요소에 대해 Jira 문제를 제출합니다. 섹션 이름 및 AWS 버전의 Red Hat OpenShift Service와 같은 구체적인 정보를 제공하십시오.
3.2. Red Hat 지식베이스 정보
Red Hat 지식베이스는 Red Hat의 제품과 기술을 최대한 활용할 수 있도록 풍부한 콘텐츠를 제공합니다. Red Hat 지식베이스는 Red Hat 제품 설치, 설정 및 사용에 대한 기사, 제품 문서 및 동영상으로 구성되어 있습니다. 또한 알려진 문제에 대한 솔루션을 검색할 수 있으며, 간결한 근본 원인 설명 및 해결 단계를 제공합니다.
3.3. Red Hat 지식베이스 검색
AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 문제가 있는 경우 초기 검색을 수행하여 Red Hat 지식베이스 내에 솔루션이 이미 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- Red Hat 고객 포털 계정이 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
- Red Hat 고객 포털에 로그인합니다.
- Search를 클릭합니다
검색 필드에서 다음을 포함하여 문제와 관련된 키워드 및 문자열을 입력합니다.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS 구성 요소 (예: etcd)
- 관련 절차 (예: installation 등)
- 명시적 실패와 관련된 경고, 오류 메시지 및 기타 출력
- Enter 키를 클릭합니다.
- 선택 사항: AWS 제품 필터에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 를 선택합니다.
- 선택 사항: 문서 콘텐츠 유형 필터를 선택합니다.
3.4. 지원 케이스 제출
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. - Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
프로세스
- Red Hat 고객 포털의 고객 지원 페이지에 로그인합니다.
- 지원 받기를 클릭합니다.
고객 지원 페이지의 케이스 탭에서 다음을 수행합니다.
- 선택 사항: 필요한 경우 미리 채워진 계정 및 소유자 세부 정보를 변경합니다.
- Bug 또는 Defect 와 같은 문제에 대한 적절한 카테고리를 선택하고 Continue 를 클릭합니다.
다음 정보를 입력합니다.
- 요약 필드에 간결하지만 설명적인 문제 요약을 입력하고 경험되는 증상에 대한 자세한 내용과 기대치를 입력합니다.
- 제품 드롭다운 메뉴에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS 를 선택합니다.
- 보고되는 문제와 관련이 있을 수 있는 권장 Red Hat 지식베이스 솔루션 목록을 확인합니다. 제안된 문서로 문제가 해결되지 않으면 Continue을 클릭합니다.
- 보고되는 문제와 관련있는 제안된 Red Hat 지식베이스 솔루션 목록을 확인하십시오. 케이스 작성 과정에서 더 많은 정보를 제공하면 목록이 구체화됩니다. 제안된 문서로 문제가 해결되지 않으면 Continue을 클릭합니다.
- 제시된 계정 정보가 정확한지 확인하고 필요한 경우 적절하게 수정합니다.
AWS Cluster ID에서 자동 입력된 Red Hat OpenShift Service가 올바른지 확인합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 클러스터 ID를 수동으로 가져옵니다.
AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 수동으로 가져오려면 다음을 수행합니다.
- 홈 → 개요 로 이동합니다.
- Details 섹션의 Cluster ID 필드에서 값을 찾습니다.
또는 AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 통해 새 지원 케이스를 열고 클러스터 ID를 자동으로 입력할 수 있습니다.
- 툴바에서 (?) Help → Open Support Case로 이동합니다.
- Cluster ID 값이 자동으로 입력됩니다.
OpenShift CLI (
oc)를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 얻으려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ oc get clusterversion -o jsonpath='{.items[].spec.clusterID}{"\n"}'
프롬프트가 표시되면 다음 질문을 입력한 후 Continue를 클릭합니다.
- 무엇을 경험하고 있습니까? 어떤 일이 발생할 것으로 예상하십니까?
- 귀하 또는 비즈니스에 미치는 영향 또는 가치를 정의합니다.
- 이 동작을 어디에서 경험하고 있습니까? 어떤 시스템 환경을 사용하고 있습니까?
- 이 동작이 언제 발생합니까? 발생 빈도는 어떻게 됩니까? 반복적으로 발생합니까? 특정 시간에만 발생합니까?
- 관련 진단 데이터 파일을 업로드하고 Continue를 클릭합니다.
- 관련 케이스 관리 세부 정보를 입력하고 Continue를 클릭합니다.
- 케이스 세부 정보를 미리보고 Submit을 클릭합니다.
3.5. 추가 리소스
- 클러스터 문제 식별에 대한 자세한 내용은 Insights를 사용하여 클러스터 문제 식별을 참조하십시오.
4장. 클러스터에 연결하여 원격 상태 모니터링
4.1. 원격 상태 모니터링 정보
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 클러스터에 대한 Telemetry 및 구성 데이터를 수집하고 Telemeter Client 및 Insights Operator를 사용하여 Red Hat에 보고합니다. Red Hat에 제공되는 데이터는 이 문서에 설명된 장점을 사용할 수 있습니다.
Telemetry 및 Insights Operator를 통해 Red Hat에 데이터를 보고하는 클러스터는 연결 클러스터(connected cluster)라고 합니다.
Telemetry 는 Red Hat이 AWS Telemeter Client의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 Red Hat으로 전송되는 정보를 설명하는 데 사용하는 용어입니다. 경량 속성은 연결된 클러스터에서 Red Hat으로 전송되어 서브스크립션 관리 자동화를 활성화하고, 클러스터의 상태를 모니터링하며, 지원 및 고객 환경을 개선합니다.
Insights Operator 는 AWS 구성 데이터에 대해 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 수집하여 Red Hat으로 전송합니다. 데이터는 클러스터가 노출될 수 있는 문제에 대한 통찰력을 생성하는 데 사용됩니다. 이러한 통찰력은 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 클러스터 관리자에게 전달됩니다.
이 두 프로세스에 대한 자세한 내용은 이 문서에 기재되어 있습니다.
Telemetry 및 Insights Operator의 이점
Telemetry 및 Insights Operator는 최종 사용자에게 다음과 같은 이점을 제공합니다.
- 문제 확인 및 해결 방법을 강화 Red Hat은 최종 사용자에 정상적으로 표시될 수 있는 이벤트를 클러스터 단위로 보다 광범위한 관점에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 일부 문제는 이러한 관점에서 보다 신속하게 확인하고 Jira 문제를 열거나 지원 케이스를 열 필요없이 최종 사용자가 해결 할 수 있습니다.
-
고급 릴리스 관리 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는
후보,빠른및안정적인릴리스 채널을 제공하여 업데이트 전략을 선택할 수 있습니다. 릴리스를fast버전에서stable버전으로 업그레이드하는 것은 업데이트의 성공률 및 업그레이드 중에 발생하는 이벤트에 따라 달라집니다. 연결된 클러스터에서 제공하는 정보를 통해 Red Hat은 릴리스 품질을stable채널로 개선하고fast채널에 있는 문제에 신속하게 대응할 수 있습니다. - 새로운 기능 및 기능의 우선 순위를 지정 수집된 데이터는 AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 가장 많이 사용되는 영역에 대한 통찰력을 제공합니다. 이러한 정보를 통해 Red Hat은 고객에게 가장 큰 영향을 미치는 새로운 기능 및 기능을 개발하는 데 중점을 둘 수 있습니다.
- 간소화된 지원 환경 제공 Red Hat 고객 포털에서 지원 티켓을 생성할 때 연결된 클러스터의 클러스터 ID를 지정할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 Red Hat은 연결된 정보를 사용하여 클러스터 고유의 간소화된 지원 환경을 제공할 수 있습니다. 이 문서에서는 향상된 지원 환경에 대한 자세한 정보를 제공합니다.
- 예측 분석 OpenShift Cluster Manager 의 클러스터에 대해 표시되는 Insights는 연결된 클러스터에서 수집한 정보로 활성화됩니다. Red Hat은 AWS 클러스터의 Red Hat OpenShift Service가 노출되는 문제를 식별하는 데 도움이 되도록 딥 러닝, 머신 러닝 및 인공 지능 자동화를 적용하는 데 투자하고 있습니다.
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 원격 상태 보고가 항상 활성화됩니다. 이를 옵트아웃할 수 없습니다.
4.1.1. Telemetry 정보
Telemetry는 엄선된 클러스터 모니터링 지표의 일부를 Red Hat으로 보냅니다. Telemeter Client는 4분 30초마다 메트릭 값을 가져와 Red Hat에 데이터를 업로드합니다. 이러한 메트릭에 대한 설명은 이 설명서에서 제공됩니다.
Red Hat은 이러한 데이터 스트림을 사용하여 클러스터를 실시간으로 모니터링하고 필요에 따라 고객에게 영향을 미치는 문제에 대응합니다. 또한 Red Hat은 AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 고객에게 제공하여 서비스 영향을 최소화하고 지속적으로 업그레이드 환경을 개선할 수 있습니다.
이러한 디버깅 정보는 Red Hat 지원 및 엔지니어링 팀에 제공되며, 지원 사례를 통해 보고된 데이터에 액세스하는 것과 동일한 제한 사항이 적용됩니다. Red Hat은 연결된 모든 클러스터 정보를 사용하여 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 개선하고 보다 직관적으로 사용할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
4.1.1.1. Telemetry에서 수집하는 정보
Telemetry에서 수집되는 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
4.1.1.1.1. 시스템 정보
- AWS 클러스터 버전의 Red Hat OpenShift Service 및 업데이트 버전 가용성 확인에 사용되는 업데이트 세부 정보를 포함한 버전 정보
- 클러스터당 사용 가능한 업데이트 수, 업데이트 진행 정보, 업데이트 진행 정보에 사용되는 채널 및 이미지 리포지터리, 업데이트에 발생하는 오류 수를 포함한 업데이트 정보
- 설치 중 생성된 임의의 고유 식별자
- Red Hat 지원이 클라우드 인프라 수준, 호스트 이름, IP 주소, Kubernetes Pod 이름, 네임스페이스 및 서비스의 노드 구성을 포함하여 고객에게 유용한 지원을 제공하는 데 도움이 되는 구성 세부 정보
- 클러스터 및 해당 조건 및 상태에 설치된 AWS 프레임워크의 Red Hat OpenShift Service
- 성능이 저하된 Operator에 대해 "관련 개체"로 나열된 모든 네임스페이스에 대한 이벤트
- 성능 저하 소프트웨어에 대한 정보
- 인증서의 유효성에 대한 정보
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS가 배포된 공급자 플랫폼의 이름 및 데이터 센터 위치
4.1.1.1.2. 크기 조정 정보
- CPU 코어 수 및 각각에 사용된 RAM 용량을 포함한 클러스터, 시스템 유형 및 머신 크기에 대한 정보
- etcd 멤버 수 및 etcd 클러스터에 저장된 오브젝트 수
- 빌드 전략 유형별 애플리케이션 빌드 수
4.1.1.1.3. 사용 정보
- 구성 요소, 기능 및 확장에 대한 사용 정보
- 기술 프리뷰 및 지원되지 않는 구성에 대한 사용량 세부 정보
Telemetry에서는 사용자 이름 또는 암호와 같은 식별 정보를 수집하지 않습니다. Red Hat은 개인 정보를 수집하지 않습니다. 개인 정보가 의도하지 않게 Red Hat에 수신된 경우 Red Hat은 이러한 정보를 삭제합니다. Telemetry 데이터가 개인 정보를 구성하는 범위까지, Red Hat의 개인정보 보호정책에 대한 자세한 내용은 Red Hat 개인정보처리방침을 참조하십시오.
4.1.1.2. 사용자 Telemetry
Red Hat은 귀하의 브라우저에서 익명화된 사용자 데이터를 수집합니다. 이 익명화된 데이터에는 Telemetry가 활성화된 모든 클러스터의 사용자가 사용하는 페이지, 기능 및 리소스 유형이 포함됩니다.
기타 고려 사항:
- 사용자 이벤트는 SHA-1 해시로 그룹화됩니다.
-
사용자의 IP 주소는
0.0.0.0으로 저장됩니다. - 사용자 이름과 IP 주소는 별도의 값으로 저장되지 않습니다.
추가 리소스
- Telemetry에서 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 수집하는 속성을 나열하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Telemetry에서 수집한 데이터 표시를 참조하십시오.
- Telemetry가 Prometheus에서 수집하는 속성 목록은 업스트림 cluster-monitoring-operator 소스 코드를 참조하십시오.
4.1.2. Insights Operator 정보
Insights Operator는 구성 및 구성 요소 오류 상태를 주기적으로 수집하고 기본적으로 이러한 데이터를 두 시간마다 Red Hat에 보고합니다. 이 정보를 통해 Red Hat은 구성 및 Telemetry를 통해 보고된 것보다 더 깊은 오류 데이터를 평가할 수 있습니다.
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service 사용자는 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console의 Insights Advisor 서비스에서 각 클러스터의 보고서를 표시할 수 있습니다. 문제가 확인된 경우 Insights는 추가 세부 정보와 가능한 경우 문제 해결 방법에 대한 단계를 제공합니다.
Insights Operator는 사용자 이름, 암호 또는 인증서와 같은 식별 정보를 수집하지 않습니다. Red Hat Insights 데이터 수집 및 제어에 대한 정보는 Red Hat Insights Data & Application Security를 참조하십시오.
Red Hat은 연결된 모든 클러스터 정보를 사용하여 다음을 수행합니다.
- 잠재적인 클러스터 문제를 확인하고 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console의 Insights Advisor 서비스에서 솔루션 및 예방 조치 제공
- 제품 및 지원 팀에 집계되고 중요한 정보를 제공하여 AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 개선
- AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 보다 직관적으로 설정
4.1.2.1. Insights Operator에 의해 수집되는 정보
Insights Operator에서 수집되는 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
- AWS 버전 및 환경에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service와 관련된 문제를 식별하는 클러스터 및 해당 구성 요소에 대한 일반 정보
- 설정한 매개변수와 관련된 잘못된 설정 및 문제를 확인하는 클러스터 구성 파일(예: 이미지 레지스트리 구성)
- 클러스터 구성 요소에서 발생하는 오류
- 실행 중인 업데이트의 진행 상태 정보 및 구성 요소의 업그레이드 상태
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS가 배포된 플랫폼(예: Amazon Web Services) 및 클러스터가 위치한 리전에 대한 세부 정보
- 별도의 TLS(Secure Hash Algorithm) 값으로 변환된 클러스터 워크로드 정보는 Red Hat이 중요한 세부 사항을 분리하지 않고 보안 및 버전 취약점에 대한 워크로드를 평가할 수 있습니다.
-
Operator에서 문제를 보고하면
openshift-*및kube-*프로젝트의 AWS Pod의 핵심 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 대한 정보가 수집됩니다. 여기에는 상태, 리소스, 보안 컨텍스트, 볼륨 정보 등이 포함됩니다.
추가 리소스
- Insights Operator 소스 코드는 확인 및 제공할 수 있습니다. Insights Operator에서 수집한 항목 목록은 Insights Operator 업스트림 프로젝트를 참조하십시오.
4.1.3. Telemetry 및 Insights Operator 데이터 흐름 이해
Telemeter Client는 Prometheus API에서 선택한 시계열 데이터를 수집합니다. 시계열 데이터는 처리하기 위해 4분 30초 마다 api.openshift.com에 업로드됩니다.
Insights Operator는 선택한 데이터를 Kubernetes API 및 Prometheus API에서 아카이브로 수집합니다. 아카이브는 처리를 위해 2시간마다 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 업로드됩니다. Insights Operator는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서도 최신 Insights 분석을 다운로드합니다. 이는 AWS 웹 콘솔의 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 개요 페이지에 포함된 Insights 상태 팝업을 채우는 데 사용됩니다.
Red Hat과의 모든 통신은 TLS(Transport Layer Security) 및 상호 인증서 인증을 사용하여 암호화된 채널을 통해 이루어집니다. 모든 데이터는 전송 및 정지 상태에서 암호화됩니다.
고객 데이터를 처리하는 시스템에 대한 액세스는 다단계 인증 및 엄격한 인증 권한에 의해 제어됩니다. 필요에 따라 액세스 권한이 부여되며 필수 작업으로 제한됩니다.
Telemetry 및 Insights Operator 데이터 흐름
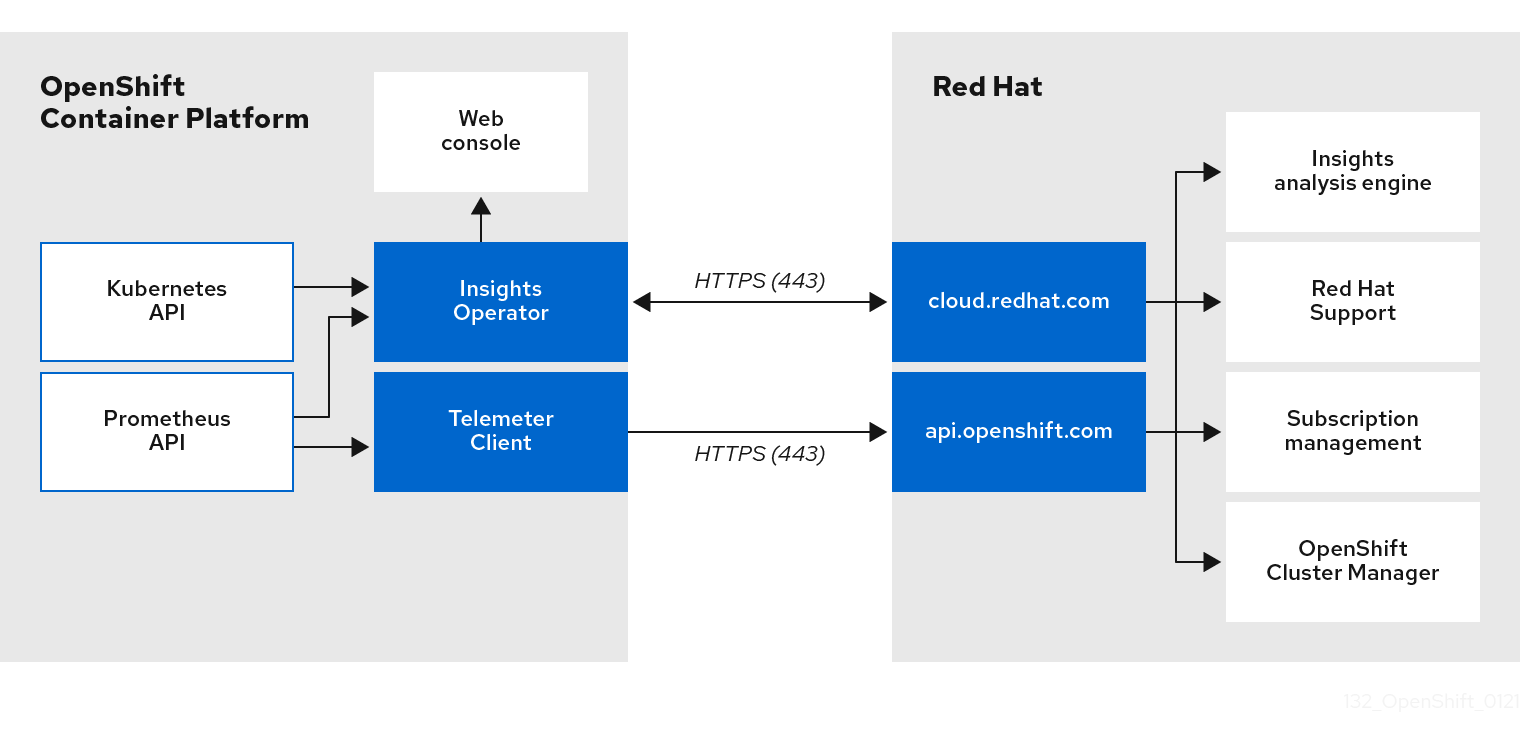
추가 리소스
- AWS 모니터링 스택의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 대한 자세한 내용은 모니터링 개요 를 참조하십시오.
4.1.4. 원격 상태 모니터링 데이터 사용 방법에 대한 추가 정보
원격 상태 모니터링을 활성화하기 위해 수집된 정보는 Telemetry에서 수집한 정보 및 Insights Operator가 수집한 정보에 자세히 설명되어 있습니다.
이 문서의 이전 섹션에 설명되어 있듯이 Red Hat은 지원 및 업그레이드, 성능 또는 구성 최적화, 서비스에 미치는 영향을 최소화, 위협 식별 및 문제 해결, 문제에 대한 대응 및 청구 등의 목적으로 Red Hat 제품 사용에 대한 데이터를 수집합니다.
수집 보안 조치
Red Hat은 Telemetry 및 구성 데이터를 보호하기 위해 설계된 기술 및 제도 상의 조치를 사용합니다.
공유
Red Hat은 사용자 환경을 개선하기 위해 Telemetry 및 Insights Operator에서 수집한 데이터를 내부적으로 공유할 수 있습니다. Red Hat은 Red Hat 제품 사용 및 고객의 사용을 보다 잘 이해할 수 있도록 돕거나 또는 파트너가 협력하여 제품의 지원을 성공적으로 통합하는 데 도움이 되는 집계 양식에서 Telemetry 및 설정 데이터를 공유할 수 있습니다.
타사
Red Hat은 Telemetry 및 구성 데이터의 수집, 분석 및 저장을 지원하기 위해 특정 타사와 협력할 수 있습니다.
4.2. 원격 상태 모니터링으로 수집된 데이터 표시
사용자 컨트롤 / Telemetry 및 설정 데이터 수집 활성화 및 비활성화
관리자는 Telemetry 및 Insights Operator에서 수집한 메트릭을 검토할 수 있습니다.
4.2.1. Telemetry로 수집한 데이터 표시
Telemetry에서 캡처한 클러스터 및 구성 요소 시계열 데이터를 볼 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
OpenShift Container Platform CLI(
oc)를 설치했습니다. -
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
프로세스
- 클러스터에 로그인합니다.
다음 명령을 실행하여 클러스터의 Prometheus 서비스를 쿼리하고 Telemetry에서 캡처한 전체 시계열 데이터 세트를 반환합니다.
$ curl -G -k -H "Authorization: Bearer $(oc whoami -t)" \ https://$(oc get route prometheus-k8s-federate -n \ openshift-monitoring -o jsonpath="{.spec.host}")/federate \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__=~"cluster:usage:.*"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="count:up0"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="count:up1"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_version"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_version_available_updates"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_version_capability"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_operator_up"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_operator_conditions"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_version_payload"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_installer"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_infrastructure_provider"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_feature_set"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_object_counts:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="ALERTS",alertstate="firing"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="code:apiserver_request_total:rate:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:capacity_cpu_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:capacity_memory_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:cpu_usage_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:memory_usage_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift:cpu_usage_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift:memory_usage_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="workload:cpu_usage_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="workload:memory_usage_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:virt_platform_nodes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:node_instance_type_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cnv:vmi_status_running:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:vmi_request_cpu_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="node_role_os_version_machine:cpu_capacity_cores:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="node_role_os_version_machine:cpu_capacity_sockets:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="subscription_sync_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="olm_resolution_duration_seconds"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="csv_succeeded"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="csv_abnormal"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:kube_persistentvolumeclaim_resource_requests_storage_bytes:provisioner:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:kubelet_volume_stats_used_bytes:provisioner:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="ceph_cluster_total_bytes"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="ceph_cluster_total_used_raw_bytes"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="ceph_health_status"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="odf_system_raw_capacity_total_bytes"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="odf_system_raw_capacity_used_bytes"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="odf_system_health_status"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:ceph_osd_metadata:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:kube_pv:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:odf_system_pvs:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:ceph_pools_iops:total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:ceph_pools_iops_bytes:total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:ceph_versions_running:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:noobaa_total_unhealthy_buckets:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:noobaa_bucket_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="job:noobaa_total_object_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="odf_system_bucket_count", system_type="OCS", system_vendor="Red Hat"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="odf_system_objects_total", system_type="OCS", system_vendor="Red Hat"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="noobaa_accounts_num"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="noobaa_total_usage"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="console_url"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:ovnkube_master_egress_routing_via_host:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:network_attachment_definition_instances:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:network_attachment_definition_enabled_instance_up:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:ingress_controller_aws_nlb_active:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:route_metrics_controller_routes_per_shard:min"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:route_metrics_controller_routes_per_shard:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:route_metrics_controller_routes_per_shard:avg"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:route_metrics_controller_routes_per_shard:median"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:openshift_route_info:tls_termination:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="insightsclient_request_send_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cam_app_workload_migrations"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:apiserver_current_inflight_requests:sum:max_over_time:2m"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:alertmanager_integrations:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:telemetry_selected_series:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift:prometheus_tsdb_head_series:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift:prometheus_tsdb_head_samples_appended_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="monitoring:container_memory_working_set_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace_job:scrape_series_added:topk3_sum1h"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace_job:scrape_samples_post_metric_relabeling:topk3"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="monitoring:haproxy_server_http_responses_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="rhmi_status"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="status:upgrading:version:rhoam_state:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="state:rhoam_critical_alerts:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="state:rhoam_warning_alerts:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="rhoam_7d_slo_percentile:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="rhoam_7d_slo_remaining_error_budget:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_legacy_scheduler_policy"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster_master_schedulable"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="che_workspace_status"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="che_workspace_started_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="che_workspace_failure_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="che_workspace_start_time_seconds_sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="che_workspace_start_time_seconds_count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cco_credentials_mode"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:kube_persistentvolume_plugin_type_counts:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="visual_web_terminal_sessions_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="acm_managed_cluster_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:vsphere_vcenter_info:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:vsphere_esxi_version_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:vsphere_node_hw_version_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift:build_by_strategy:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="rhods_aggregate_availability"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="rhods_total_users"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_disk_wal_fsync_duration_seconds:histogram_quantile",quantile="0.99"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_network_peer_round_trip_time_seconds:histogram_quantile",quantile="0.99"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_mvcc_db_total_size_in_use_in_bytes:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="instance:etcd_disk_backend_commit_duration_seconds:histogram_quantile",quantile="0.99"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="jaeger_operator_instances_storage_types"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="jaeger_operator_instances_strategies"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="jaeger_operator_instances_agent_strategies"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="appsvcs:cores_by_product:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="nto_custom_profiles:count"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift_csi_share_configmap"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift_csi_share_secret"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift_csi_share_mount_failures_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="openshift_csi_share_mount_requests_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:velero_backup_total:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:velero_restore_total:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="eo_es_storage_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="eo_es_redundancy_policy_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="eo_es_defined_delete_namespaces_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="eo_es_misconfigured_memory_resources_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:eo_es_data_nodes_total:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:eo_es_documents_created_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:eo_es_documents_deleted_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="pod:eo_es_shards_total:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="eo_es_cluster_management_state_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="imageregistry:imagestreamtags_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="imageregistry:operations_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="log_logging_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="log_collector_error_count_total"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="log_forwarder_pipeline_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="log_forwarder_input_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="log_forwarder_output_info"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:log_collected_bytes_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:log_logged_bytes_total:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="cluster:kata_monitor_running_shim_count:sum"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="platform:hypershift_hostedclusters:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="platform:hypershift_nodepools:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_unhealthy_bucket_claims:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_buckets_claims:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_unhealthy_namespace_resources:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_namespace_resources:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_unhealthy_namespace_buckets:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_namespace_buckets:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_accounts:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_usage:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="namespace:noobaa_system_health_status:max"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="ocs_advanced_feature_usage"}' \ --data-urlencode 'match[]={__name__="os_image_url_override:sum"}'
4.3. Insights를 사용하여 클러스터의 문제 식별
Insights는 Insights Operator가 전송하는 데이터를 반복적으로 분석합니다. AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 사용자는 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console의 Insights Advisor 서비스에 보고서를 표시할 수 있습니다.
4.3.1. AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service용 Red Hat Insights Advisor 정보
Insights Advisor를 사용하여 AWS 클러스터에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 상태를 평가하고 모니터링할 수 있습니다. 개별 클러스터에 대한 관심이 있거나 전체 인프라에 관계없이 서비스 가용성, 내결함성, 성능 또는 보안에 영향을 줄 수 있는 문제에 대한 클러스터 인프라 노출을 인식하는 것이 중요합니다.
Insights Operator에서 수집한 클러스터 데이터를 사용하여 Insights는 해당 데이터를 권장 라이브러리와 반복적으로 비교합니다. 각 권장 사항은 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 AWS 클러스터에 그대로 둘 수 있는 클러스터 환경 조건 집합입니다. Insights 분석 결과는 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console의 Insights Advisor 서비스에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 콘솔에서 다음 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 특정 권장 사항의 영향을 받는 클러스터를 참조하십시오.
- 강력한 필터링 기능을 사용하여 결과를 해당 권장 사항으로 구체화합니다.
- 개별 권장 사항, 존재하는 위험에 대한 세부 정보, 개별 클러스터에 맞게 조정된 해결 방법에 대해 자세히 알아보십시오.
- 다른 이해 관계자와 결과를 공유하십시오.
4.3.2. Insights Advisor 권장 사항 이해
Insights Advisor는 클러스터의 서비스 가용성, 내결함성, 성능 또는 보안에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있는 다양한 클러스터 상태 및 구성 구성 구성에 대한 정보를 번들로 제공합니다. 이 정보는 Insights Advisor의 권장 사항이라고 하며 다음 정보를 포함합니다.
- 이름: 권장 사항에 대한 간결한 설명
- 추가: Insights Advisor 아카이브에 권장 사항이 게시되었을 때
- 카테고리: 문제가 서비스 가용성, 내결함성, 성능 또는 보안에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있는지 여부
- 총 위험: 상태가 인프라에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 가능성을 기반으로 파생된 값과 이것이 발생하는 경우 운영에 미치는 영향
- 클러스터: 권장 사항이 감지되는 클러스터 목록
- 설명: 클러스터에 미치는 영향을 포함하여 문제에 대한 간략한 개요
- 관련 주제로 링크: 문제에 대한 Red Hat의 추가 정보
4.3.3. 클러스터와 관련된 잠재적인 문제 표시
이 섹션에서는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 의 Insights 권고에 Insights 보고서를 표시하는 방법을 설명합니다.
Insights는 반복적으로 클러스터를 분석하여 최신 결과를 표시합니다. 예를 들어 문제를 해결하거나 새로운 문제가 발견된 경우 이러한 결과가 변경될 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 클러스터는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 등록되어 있습니다.
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 Advisor → Recommendations 로 이동합니다.
결과에 따라 Insights Advisor는 다음 중 하나를 표시합니다.
- Insights에서 문제를 식별하지 않은 경우 일치하는 권장 사항을 찾을 수 없습니다.
- Insights가 감지한 문제 목록으로 위험(낮음, 중간, 중요 및 심각)으로 그룹화되어 있습니다.
- Insights 가 아직 클러스터를 분석하지 않은 경우 아직 클러스터가 없습니다. 클러스터가 설치, 등록 및 인터넷에 연결된 직후 분석이 시작됩니다.
문제가 표시되면 항목 앞의 > 아이콘을 클릭하여 자세한 내용을 확인합니다.
문제에 따라 세부 정보에는 문제에 대한 Red Hat의 자세한 정보 링크가 포함될 수 있습니다.
4.3.4. 모든 Insights 권고 권장 사항 표시
기본적으로 권장 사항 보기는 클러스터에서 탐지된 권장 사항만 표시합니다. 그러나 모든 권장 사항은 가상 머신 아카이브에서 볼 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- 클러스터는 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console에 등록되어 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 Advisor → Recommendations 로 이동합니다.
영향을 받는 클러스터 및 상태 필터 옆에 있는 X 아이콘을 클릭합니다.
이제 클러스터에 대한 모든 잠재적인 권장 사항을 확인할 수 있습니다.
4.3.5. Advisor 권장 필터
Insights 권고 서비스는 많은 권장 사항을 반환할 수 있습니다. 가장 중요한 권장 사항에 중점을 두려면 Advisor 권장 사항 목록에 필터를 적용하여 우선순위가 낮은 권장 사항을 제거할 수 있습니다.
기본적으로 필터는 하나 이상의 클러스터에 영향을 미치는 활성화된 권장 사항만 표시하도록 설정됩니다. Insights 라이브러리의 모든 또는 비활성화된 권장 사항을 보려면 필터를 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
필터를 적용하려면 필터 유형을 선택한 다음 드롭다운 목록에서 사용할 수 있는 옵션을 기반으로 값을 설정합니다. 권장 사항 목록에 여러 필터를 적용할 수 있습니다.
다음 필터 유형을 설정할 수 있습니다.
- name: 이름으로 권장 사항을 검색합니다.
- 총 위험: 심각,중요,보통 및 낮음 에서 하나 이상의 값을 선택하여 클러스터에 미치는 부정적인 영향을 미치는 가능성과 심각도를 나타냅니다.
- 영향: 클러스터 작업의 연속성에 미치는 영향을 나타내는 심각,높음,중간 및 낮음 에서 하나 이상의 값을 선택합니다.
- 가능성: 심각,높음,중간, 낮음 에서 하나 이상의 값을 선택하여 클러스터에 부정적인 영향을 미칠 가능성이 있는지 여부를 나타냅니다.
- 범주: Service Availability,Performance,Fault Tolerance,Security, Best Practice 에서 하나 이상의 카테고리를 선택하여 집중할 수 있습니다.
- 상태: 활성화된 권장 사항(기본값), 비활성화된 권장 사항 또는 모든 권장 사항을 표시하려면 라디오 버튼을 클릭합니다.
- 영향을 받는 클러스터: 현재 하나 이상의 클러스터, 영향을 받지 않는 권장 사항 또는 모든 권장 사항에 영향을 미치는 권장 사항을 표시하도록 필터를 설정합니다.
- 변경 위험: High,Moderate,Low y low 에서 하나 이상의 값을 선택하여 해상도 구현이 클러스터 작업에 미칠 수 있는 위험을 나타냅니다.
4.3.5.1. Insights 권고 권장 사항 필터링
AWS 클러스터 관리자의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 권장 사항 목록에 표시되는 권장 사항을 필터링할 수 있습니다. 필터를 적용하면 보고된 권장 사항 수를 줄이고 가장 높은 우선 순위 권장 사항에 집중할 수 있습니다.
다음 절차에서는 카테고리 필터를 설정하고 제거하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 그러나 절차는 모든 필터 유형과 각 값에 적용할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
OpenShift Cluster Manager Hybrid Cloud Console 에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console → OpenShift → Advisor 권장 사항으로 이동합니다.
- 기본 필터 유형 드롭다운 목록에서 카테고리 필터 유형을 선택합니다.
- filter-value 드롭다운 목록을 펼치고 보려는 각 범주의 권장 사항 옆에 있는 확인란을 선택합니다. 불필요한 카테고리에 대해 확인란을 지웁니다.
- 선택 사항: 목록을 추가로 구체화하려면 필터를 추가합니다.
선택한 범주의 권장 사항만 목록에 표시됩니다.
검증
- 필터를 적용한 후 업데이트된 권장 사항 목록을 볼 수 있습니다. 적용된 필터는 기본 필터 옆에 추가됩니다.
4.3.5.2. Insights Advisor 권장 사항에서 필터 제거
권장 사항 목록에 여러 필터를 적용할 수 있습니다. 준비가 되면 개별적으로 제거하거나 완전히 재설정할 수 있습니다.
개별적으로 필터 제거
- 기본 필터를 포함하여 각 필터 옆에 있는 X 아이콘을 클릭하여 개별적으로 제거합니다.
기본이 아닌 모든 필터 제거
- 새로 고침 필터 를 클릭하여 적용한 필터만 제거하고 기본 필터를 그대로 둡니다.
4.3.6. Insights 권고 권장 사항 비활성화
보고서에 더 이상 표시되지 않도록 클러스터에 영향을 미치는 특정 권장 사항을 비활성화할 수 있습니다. 단일 클러스터 또는 모든 클러스터에 대한 권장 사항을 비활성화할 수 있습니다.
모든 클러스터에 대한 권장 사항을 비활성화하는 것은 향후 클러스터에도 적용됩니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- 클러스터는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 등록되어 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 Advisor → Recommendations 로 이동합니다.
- 선택 사항: 필요에 따라 클러스터에 영향을 미치는 상태 필터를 사용합니다.
다음 방법 중 하나를 사용하여 경고를 비활성화합니다.
경고를 비활성화하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
-
해당 경고에 대한 옵션 메뉴
 를 클릭한 다음 권장 사항 비활성화 를 클릭합니다.
를 클릭한 다음 권장 사항 비활성화 를 클릭합니다.
- 확인 참고 사항을 입력하고 저장을 클릭합니다.
-
해당 경고에 대한 옵션 메뉴
경고를 비활성화하기 전에 이 경고의 영향을 받는 클러스터를 보려면 다음을 수행합니다.
- 비활성화할 권장 사항 이름을 클릭합니다. 단일 권장 사항 페이지로 이동합니다.
- 영향을 받는 클러스터 섹션의 클러스터 목록을 검토합니다.
- 동작 → 권장 사항 비활성화 를 클릭하여 모든 클러스터에 대한 경고를 비활성화합니다.
- 확인 참고 사항을 입력하고 저장을 클릭합니다.
4.3.7. 이전에 비활성화된 Insights Advisor 권장 사항 활성화
모든 클러스터에 대해 권장 사항이 비활성화되면 더 이상 Insights 권고에 권장 사항이 표시되지 않습니다. 이 동작을 변경할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- 클러스터는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 등록되어 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 에서 Advisor → Recommendations 로 이동합니다.
비활성화된 권장 사항에 표시할 권장 사항을 필터링합니다.
- Status 드롭다운 메뉴에서 Status 를 선택합니다.
- Filter by status 드롭다운 메뉴에서 Disabled 를 선택합니다.
- 선택 사항: 영향을 받는 클러스터 필터를 지웁니다.
- 활성화할 권장 사항을 찾습니다.
-
옵션 메뉴
 를 클릭한 다음 권장 사항 사용을 클릭합니다.
를 클릭한 다음 권장 사항 사용을 클릭합니다.
4.3.8. 웹 콘솔에 Insights 상태 표시
Insights는 클러스터를 반복적으로 분석하고 AWS 웹 콘솔의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 확인된 잠재적 클러스터 문제의 상태를 표시할 수 있습니다. 이 상태에는 다양한 카테고리의 문제 수가 표시되고 자세한 내용은 OpenShift Cluster Manager 의 보고서에 대한 링크입니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 클러스터는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 등록되어 있습니다.
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 로그인되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- AWS 웹 콘솔의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 홈 → 개요 로 이동합니다.
상태 카드에서 Insights를 클릭합니다.
팝업 창에 잠재적인 문제가 위험으로 그룹화되어 나열됩니다. 개별 카테고리를 클릭하거나 Insights Advisor의 모든 권장 사항 보기를 클릭하여 자세한 내용을 표시합니다.
4.4. Insights Operator 사용
Insights Operator는 구성 및 구성 요소 오류 상태를 주기적으로 수집하고 기본적으로 이러한 데이터를 두 시간마다 Red Hat에 보고합니다. 이 정보를 통해 Red Hat은 구성 및 Telemetry를 통해 보고된 것보다 더 깊은 오류 데이터를 평가할 수 있습니다. AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 사용자는 Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console의 Insights Advisor 서비스에 보고서를 표시할 수 있습니다.
추가 리소스
- Insights Advisor를 사용하여 클러스터 문제를 식별하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Insights를 사용하여 클러스터 문제 식별을 참조하십시오.
4.4.1. Insights Operator 경고 이해
Insights Operator는 Prometheus 모니터링 시스템을 통해 Alertmanager에 경고를 선언합니다. 다음 방법 중 하나를 사용하여 AWS 웹 콘솔의 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 경고 UI에서 이러한 경고를 볼 수 있습니다.
- 관리자 관점에서 모니터링 → 경고를 클릭합니다.
- 개발자 화면에서 모니터링 → <project_name> → 경고 탭을 클릭합니다.
현재 조건이 충족되면 Insights Operator에서 다음 경고를 보냅니다.
표 4.1. Insights Operator 경고
| 경고 | 설명 |
|---|---|
|
| Insights Operator가 비활성화되어 있습니다. |
|
| Red Hat 서브스크립션 관리에서는 간단한 컨텐츠 액세스가 허용되지 않습니다. |
|
| Insights에는 클러스터에 대한 활성 권장 사항이 있습니다. |
4.4.2. Deployment Validation Operator 데이터 난독 처리
Operator가 설치된 경우 클러스터 관리자는 DVO(Deployment Validation Operator)에서 데이터를 난독화하도록 Cryostat Operator를 구성할 수 있습니다. workload_names 값이 insights-config ConfigMap 오브젝트에 추가되면 UID보다 워크로드 이름-rather가 Openshift의 Insights에 표시되어 클러스터 관리자가 더 잘 인식할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- 원격 상태 보고가 활성화되어 있습니다 (기본값).
- "cluster-admin" 역할을 사용하여 AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 로그인했습니다.
-
insights-config
ConfigMap오브젝트는openshift-insights네임스페이스에 있습니다. - 클러스터가 자체 관리되고 Deployment Validation Operator가 설치됩니다.
프로세스
- 워크로드 → ConfigMaps 로 이동하여 Project: openshift-insights 를 선택합니다.
-
insights-config
ConfigMap오브젝트를 클릭하여 엽니다. - 작업을 클릭하고 ConfigMap 편집을 선택합니다.
- YAML 보기 라디오 버튼을 클릭합니다.
파일에서
workload_names값을 사용하여난독 처리속성을 설정합니다.apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap # ... data: config.yaml: | dataReporting: obfuscation: - workload_names # ...- 저장을 클릭합니다. insights-config config-map 세부 정보 페이지가 열립니다.
-
config.yaml난독 처리속성 값이- workload_names로 설정되어 있는지 확인합니다.
5장. 클러스터에 대한 데이터 수집
다음 툴을 사용하여 AWS 클러스터에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 대한 디버깅 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.
5.1. must-gather 툴 정보
oc adm must-gather CLI 명령은 다음을 포함하여 문제를 디버깅하는 데 필요할 가능성이 높은 클러스터에서 정보를 수집합니다.
- 리소스 정의
- 서비스 로그
기본적으로 oc adm must-gather 명령은 기본 플러그인 이미지를 사용하고 ./must-gather.local 에 씁니다.
또는 다음 섹션에 설명된 대로 적절한 인수로 명령을 실행하여 특정 정보를 수집할 수 있습니다.
하나 이상의 특정 기능과 관련된 데이터를 수집하려면 다음 섹션에 나열된 대로 이미지와 함께
--image인수를 사용합니다.예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
$ oc adm must-gather \ --image=registry.redhat.io/container-native-virtualization/cnv-must-gather-rhel9:v4.15.1
감사 로그를 수집하려면 다음 섹션에 설명된 대로
-- /usr/bin/gather_audit_logs인수를 사용하십시오.예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
$ oc adm must-gather -- /usr/bin/gather_audit_logs
참고감사 로그는 파일 크기를 줄이기 위해 기본 정보 세트의 일부로 수집되지 않습니다.
oc adm must-gather 를 실행하면 클러스터의 새 프로젝트에 임의의 이름이 있는 새 Pod가 생성됩니다. 해당 Pod에서 데이터가 수집되어 현재 작업 디렉터리에 must-gather.local 로 시작하는 새 디렉터리에 저장됩니다.
예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ... openshift-must-gather-5drcj must-gather-bklx4 2/2 Running 0 72s openshift-must-gather-5drcj must-gather-s8sdh 2/2 Running 0 72s ...
필요한 경우 --run-namespace 옵션을 사용하여 특정 네임스페이스에서 oc adm must-gather 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다.
예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
$ oc adm must-gather --run-namespace <namespace> \ --image=registry.redhat.io/container-native-virtualization/cnv-must-gather-rhel9:v4.15.1
5.1.1. Red Hat 지원을 위한 클러스터에 대한 데이터 수집
oc adm must-gather CLI 명령을 사용하여 클러스터에 대한 디버깅 정보를 수집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
-
must-gather데이터를 저장하려는 디렉터리로 이동합니다. oc adm must-gather명령을 실행합니다.$ oc adm must-gather
참고이 명령은 기본적으로 임의의 컨트롤 플레인 노드를 선택하므로 Pod가
NotReady및SchedulingDisabled상태인 컨트롤 플레인 노드로 예약할 수 있습니다.예를 들어 클러스터에서 Pod를 예약할 수 없는 경우와 같이 명령이 실패하면
oc adm inspect명령을 사용하여 특정 리소스에 대한 정보를 수집합니다.참고권장되는 리소스를 얻으려면 Red Hat 지원에 문의하십시오.
작업 디렉토리에서 생성된
must-gather디렉토리에서 압축 파일을 만듭니다. 예를 들어 Linux 운영 체제를 사용하는 컴퓨터에서 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ tar cvaf must-gather.tar.gz must-gather.local.5421342344627712289/ 1- 1
must-gather-local.5421342344627712289/를 실제 디렉터리 이름으로 교체하십시오.
- 압축 파일을 Red Hat 고객 포털 의 고객 지원 페이지의 지원 케이스에 첨부합니다.
5.1.2. 특정 기능에 대한 데이터 수집
oc adm must-gather CLI 명령을 --image 또는 --image-stream 인수와 함께 사용하여 특정 기능에 대한 디버깅 정보를 수집할 수 있습니다. must-gather 툴은 여러 이미지를 지원하므로 단일 명령을 실행하여 둘 이상의 기능에 대한 데이터를 수집할 수 있습니다.
표 5.1. 지원되는 must-gather 이미지
| 이미지 | 목적 |
|---|---|
|
| OpenShift Virtualization의 데이터 수집. |
|
| OpenShift Serverless의 데이터 수집. |
|
| Red Hat OpenShift Service Mesh의 데이터 수집 |
|
| Migration Toolkit for Containers의 데이터 수집 |
|
| 로깅을 위한 데이터 수집 |
|
| OpenShift Shared Resource CSI 드라이버의 데이터 수집 |
|
| Red Hat OpenShift GitOps의 데이터 수집 |
|
| Secrets Store CSI Driver Operator의 데이터 수집 |
|
| RHACM(Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management) 2.10 이상의 데이터 수집 |
|
| RHACM 2.9 및 이전 버전의 데이터 수집 |
|
| 연결이 끊긴 환경에서 RHACM 2.10 이상의 데이터 수집 |
|
| 연결이 끊긴 환경에서 RHACM 2.9 및 이전 버전의 데이터 수집 |
AWS 구성 요소의 이미지에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 최신 버전을 확인하려면 Red Hat 고객 포털의 OpenShift Operator 라이프 사이클 웹 페이지를 참조하십시오.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
-
must-gather데이터를 저장하려는 디렉터리로 이동합니다. --image또는--image-stream인수를 하나 이상 사용하여oc adm must-gather명령을 실행합니다.참고-
특정 기능 데이터 외에도 기본
must-gather데이터를 수집하려면--image-stream=openshift/must-gather인수를 추가하십시오.
예를 들어 다음 명령은 기본 클러스터 데이터와 OpenShift Virtualization 관련 정보를 모두 수집합니다.
$ oc adm must-gather \ --image-stream=openshift/must-gather \ 1 --image=registry.redhat.io/container-native-virtualization/cnv-must-gather-rhel9:v4.15.1 2
must-gather툴을 추가 인수와 함께 사용하여 클러스터의 OpenShift 로깅 및 Red Hat OpenShift Logging Operator와 관련된 데이터를 수집할 수 있습니다. OpenShift 로깅의 경우 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ oc adm must-gather --image=$(oc -n openshift-logging get deployment.apps/cluster-logging-operator \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.template.spec.containers[?(@.name == "cluster-logging-operator")].image}')예 5.1. OpenShift 로깅의
must-gather출력 예├── cluster-logging │ ├── clo │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator-74dd5994f-6ttgt │ │ ├── clusterlogforwarder_cr │ │ ├── cr │ │ ├── csv │ │ ├── deployment │ │ └── logforwarding_cr │ ├── collector │ │ ├── fluentd-2tr64 │ ├── eo │ │ ├── csv │ │ ├── deployment │ │ └── elasticsearch-operator-7dc7d97b9d-jb4r4 │ ├── es │ │ ├── cluster-elasticsearch │ │ │ ├── aliases │ │ │ ├── health │ │ │ ├── indices │ │ │ ├── latest_documents.json │ │ │ ├── nodes │ │ │ ├── nodes_stats.json │ │ │ └── thread_pool │ │ ├── cr │ │ ├── elasticsearch-cdm-lp8l38m0-1-794d6dd989-4jxms │ │ └── logs │ │ ├── elasticsearch-cdm-lp8l38m0-1-794d6dd989-4jxms │ ├── install │ │ ├── co_logs │ │ ├── install_plan │ │ ├── olmo_logs │ │ └── subscription │ └── kibana │ ├── cr │ ├── kibana-9d69668d4-2rkvz ├── cluster-scoped-resources │ └── core │ ├── nodes │ │ ├── ip-10-0-146-180.eu-west-1.compute.internal.yaml │ └── persistentvolumes │ ├── pvc-0a8d65d9-54aa-4c44-9ecc-33d9381e41c1.yaml ├── event-filter.html ├── gather-debug.log └── namespaces ├── openshift-logging │ ├── apps │ │ ├── daemonsets.yaml │ │ ├── deployments.yaml │ │ ├── replicasets.yaml │ │ └── statefulsets.yaml │ ├── batch │ │ ├── cronjobs.yaml │ │ └── jobs.yaml │ ├── core │ │ ├── configmaps.yaml │ │ ├── endpoints.yaml │ │ ├── events │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-app-1596020400-gm6nl.1626341a296c16a1.yaml │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-audit-1596020400-9l9n4.1626341a2af81bbd.yaml │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-infra-1596020400-v98tk.1626341a2d821069.yaml │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-app-1596020400-cc5vc.1626341a3019b238.yaml │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-audit-1596020400-s8d5s.1626341a31f7b315.yaml │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-infra-1596020400-7mgv8.1626341a35ea59ed.yaml │ │ ├── events.yaml │ │ ├── persistentvolumeclaims.yaml │ │ ├── pods.yaml │ │ ├── replicationcontrollers.yaml │ │ ├── secrets.yaml │ │ └── services.yaml │ ├── openshift-logging.yaml │ ├── pods │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator-74dd5994f-6ttgt │ │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator │ │ │ │ └── cluster-logging-operator │ │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ │ └── cluster-logging-operator-74dd5994f-6ttgt.yaml │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator-registry-6df49d7d4-mxxff │ │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator-registry │ │ │ │ └── cluster-logging-operator-registry │ │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ │ ├── cluster-logging-operator-registry-6df49d7d4-mxxff.yaml │ │ │ └── mutate-csv-and-generate-sqlite-db │ │ │ └── mutate-csv-and-generate-sqlite-db │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ ├── elasticsearch-cdm-lp8l38m0-1-794d6dd989-4jxms │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-app-1596030300-bpgcx │ │ │ ├── elasticsearch-im-app-1596030300-bpgcx.yaml │ │ │ └── indexmanagement │ │ │ └── indexmanagement │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ ├── fluentd-2tr64 │ │ │ ├── fluentd │ │ │ │ └── fluentd │ │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ │ ├── fluentd-2tr64.yaml │ │ │ └── fluentd-init │ │ │ └── fluentd-init │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ ├── kibana-9d69668d4-2rkvz │ │ │ ├── kibana │ │ │ │ └── kibana │ │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ │ └── previous.log │ │ │ ├── kibana-9d69668d4-2rkvz.yaml │ │ │ └── kibana-proxy │ │ │ └── kibana-proxy │ │ │ └── logs │ │ │ ├── current.log │ │ │ ├── previous.insecure.log │ │ │ └── previous.log │ └── route.openshift.io │ └── routes.yaml └── openshift-operators-redhat ├── ...-
특정 기능 데이터 외에도 기본
--image또는--image-stream인수를 하나 이상 사용하여oc adm must-gather명령을 실행합니다. 예를 들어 다음 명령은 기본 클러스터 데이터와 KubeVirt 관련 정보를 모두 수집합니다.$ oc adm must-gather \ --image-stream=openshift/must-gather \ 1 --image=quay.io/kubevirt/must-gather 2
작업 디렉토리에서 생성된
must-gather디렉토리에서 압축 파일을 만듭니다. 예를 들어 Linux 운영 체제를 사용하는 컴퓨터에서 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ tar cvaf must-gather.tar.gz must-gather.local.5421342344627712289/ 1- 1
must-gather-local.5421342344627712289/를 실제 디렉터리 이름으로 교체하십시오.
- 압축 파일을 Red Hat 고객 포털 의 고객 지원 페이지의 지원 케이스에 첨부합니다.
5.2. 추가 리소스
5.2.1. 네트워크 로그 수집
클러스터의 모든 노드에서 네트워크 로그를 수집할 수 있습니다.
프로세스
-- gather_network_logs를 사용하여oc adm must-gather명령을 실행합니다.$ oc adm must-gather -- gather_network_logs
참고기본적으로
must-gather툴은 클러스터의 모든 노드에서 OVNnbdb및sbdb데이터베이스를 수집합니다. OVNnbdb데이터베이스에 대한 OVN-Kubernetes 트랜잭션이 포함된 추가 로그를 포함하도록-- gather_network_logs옵션을 추가합니다.작업 디렉토리에서 생성된
must-gather디렉토리에서 압축 파일을 만듭니다. 예를 들어 Linux 운영 체제를 사용하는 컴퓨터에서 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ tar cvaf must-gather.tar.gz must-gather.local.472290403699006248 1- 1
must-gather-local.472290403699006248을 실제 디렉터리 이름으로 교체합니다.
- 압축 파일을 Red Hat 고객 포털 의 고객 지원 페이지의 지원 케이스에 첨부합니다.
5.2.2. must-gather 스토리지 제한 변경
oc adm must-gather 명령을 사용하여 데이터를 수집할 때 정보의 기본 최대 스토리지는 컨테이너의 스토리지 용량의 30%입니다. 30% 제한에 도달하면 컨테이너가 종료되고 수집 프로세스가 중지됩니다. 이미 수집된 정보는 로컬 스토리지에 다운로드되어 있습니다. must-gather 명령을 다시 실행하려면 스토리지 용량이 더 많은 컨테이너를 사용하거나 최대 볼륨 백분율을 조정해야 합니다.
컨테이너가 스토리지 제한에 도달하면 다음 예와 유사한 오류 메시지가 생성됩니다.
출력 예
Disk usage exceeds the volume percentage of 30% for mounted directory. Exiting...
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
volume-percentage플래그를 사용하여oc adm must-gather명령을 실행합니다. 새 값은 100을 초과할 수 없습니다.$ oc adm must-gather --volume-percentage <storage_percentage>
5.3. 클러스터 ID 검색
Red Hat 지원에 정보를 제공할 때 클러스터의 고유 식별자를 제공하는 것이 유용합니다. AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 자동으로 입력할 수 있습니다. 웹 콘솔 또는 OpenShift CLI (oc)를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 수동으로 검색할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
설치된 웹 콘솔 또는 OpenShift CLI(
oc)에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
프로세스
OpenShift Cluster Manager 를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 수동으로 가져오려면 다음을 수행합니다.
- 클러스터로 이동합니다.
- 지원 케이스를 열어야 하는 클러스터 이름을 클릭합니다.
- 개요 탭의 세부 정보 섹션에 있는 Cluster ID 필드에서 값을 찾습니다.
웹 콘솔을 사용하여 지원 케이스를 열고 클러스터 ID를 자동으로 입력하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
- 툴바에서 (?) Help 를 선택하고 목록에서 피드백 공유를 선택합니다.
- 경험 창에 대해 Tell us에서 지원 케이스 열기 를 클릭합니다.
웹 콘솔을 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 수동으로 가져오려면 다음을 수행합니다.
- 홈 → 개요 로 이동합니다.
- 값은 Details 섹션의 Cluster ID 필드에서 사용 가능합니다.
OpenShift CLI (
oc)를 사용하여 클러스터 ID를 얻으려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ oc get clusterversion -o jsonpath='{.items[].spec.clusterID}{"\n"}'
5.4. 클러스터 노드의 저널 로그 쿼리
개별 클러스터 노드의 /var/log 내에 journald 장치 로그 및 기타 로그를 수집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
AWS 클러스터 노드의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서
kubeletjournald장치 로그를 쿼리합니다. 다음 예제에서는 컨트롤 플레인 노드만 쿼리합니다.$ oc adm node-logs --role=master -u kubelet 1- 1
- 다른 장치 로그를 쿼리하려면
kubelet을 적절하게 대체합니다.
클러스터 노드의
/var/log/아래에있는 특정 하위 디렉터리에서 로그를 수집합니다./var/log/하위 디렉토리에 포함된 로그 목록을 검색합니다. 다음 예제는 모든 컨트롤 플레인 노드의/var/log/openshift-apiserver/에 있는 파일을 나열합니다.$ oc adm node-logs --role=master --path=openshift-apiserver
/var/log/하위 디렉터리 내의 특정 로그를 확인합니다. 다음 예제는 모든 컨트롤 플레인 노드에서/var/log/openshift-apiserver/audit.log내용을 출력합니다.$ oc adm node-logs --role=master --path=openshift-apiserver/audit.log
5.5. 네트워크 추적 방법
패킷 캡처 레코드 형태로 네트워크 추적을 수집하면 네트워크 문제 해결과 관련하여 Red Hat 지원을 지원할 수 있습니다.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS는 네트워크 추적을 수행하는 두 가지 방법을 지원합니다. 다음 표를 검토하고 요구 사항에 맞는 방법을 선택합니다.
표 5.2. 네트워크 추적을 수집하는 지원되는 방법
| 방법 | 이점 및 기능 |
|---|---|
| 호스트 네트워크 추적 수집 | 하나 이상의 노드에 동시에 지정하는 기간에 대해 패킷 캡처를 수행합니다. 지정된 기간이 충족되면 패킷 캡처 파일이 노드에서 클라이언트 시스템으로 전송됩니다. 특정 작업에서 네트워크 통신 문제를 트리거하는 이유를 해결할 수 있습니다. 패킷 캡처를 실행하고 문제를 트리거하는 작업을 수행하고 로그를 사용하여 문제를 진단합니다. |
| AWS 노드 또는 컨테이너의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 네트워크 추적 수집 |
하나의 노드 또는 하나의 컨테이너에서 패킷 캡처를 수행합니다. 패킷 캡처를 수동으로 시작하고 네트워크 통신 문제를 트리거한 다음 패킷 캡처를 수동으로 중지할 수 있습니다.
이 방법은 |
5.5.1. 호스트 네트워크 추적 수집
네트워크 통신을 추적하고 동시에 여러 노드에서 패킷을 캡처하여 네트워크 관련 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
oc adm must-gather 명령과 registry.redhat.io/openshift4/network-tools-rhel8 컨테이너 이미지 조합을 사용하여 노드에서 패킷 캡처를 수집할 수 있습니다. 패킷 캡처를 분석하면 네트워크 통신 문제를 해결하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
oc adm must-gather 명령은 특정 노드의 Pod에서 tcpdump 명령을 실행하는 데 사용됩니다. tcpdump 명령은 Pod에 패킷 캡처를 기록합니다. tcpdump 명령이 종료되면 oc adm must-gather 명령은 Pod에서 패킷 캡처가 있는 파일을 클라이언트 머신으로 전송합니다.
다음 절차의 샘플 명령은 tcpdump 명령을 사용하여 패킷 캡처를 수행하는 방법을 보여줍니다. 그러나 --image 인수에 지정된 컨테이너 이미지에서 모든 명령을 실행하여 여러 노드에서 문제 해결 정보를 동시에 수집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 로그인되어 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
다음 명령을 실행하여 일부 노드에서 호스트 네트워크에서 패킷 캡처를 실행합니다.
$ oc adm must-gather \ --dest-dir /tmp/captures \ <.> --source-dir '/tmp/tcpdump/' \ <.> --image registry.redhat.io/openshift4/network-tools-rhel8:latest \ <.> --node-selector 'node-role.kubernetes.io/worker' \ <.> --host-network=true \ <.> --timeout 30s \ <.> -- \ tcpdump -i any \ <.> -w /tmp/tcpdump/%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.pcap -W 1 -G 300<.>
--dest-dir인수는oc adm must-gather가 클라이언트 머신의/tmp/captures와 관련된 디렉터리에 패킷 캡처를 저장하도록 지정합니다. 쓰기 가능한 디렉터리를 지정할 수 있습니다. <.>oc adm must-gather가 시작되는 디버그 Pod에서tcpdump가 실행될 때--source-dir인수는 패킷 캡처가 Pod의/tmp/tcpdump디렉터리에 일시적으로 저장되도록 지정합니다. <.>--image인수는tcpdump명령을 포함하는 컨테이너 이미지. <.>--node-selector인수 및 예제 값은 작업자 노드에서 패킷 캡처를 수행하도록 지정합니다. 또는 단일 노드에서 패킷 캡처를 실행하도록--node-name인수를 지정할 수 있습니다.--node-selector및--node-name인수를 모두 생략하면 패킷 캡처가 모든 노드에서 수행됩니다. <.> 패킷 캡처가 노드의 네트워크 인터페이스에서 수행되도록--host-network=true인수가 필요합니다. <.>--timeout인수 및 값은 디버그 Pod를 30 초 동안 실행하기 위해 지정합니다.--timeout인수와 기간을 지정하지 않으면 디버그 Pod가 10분 동안 실행됩니다. <.>tcpdump명령의-i any인수는 모든 네트워크 인터페이스에서 패킷을 캡처하도록 지정합니다. 또는 네트워크 인터페이스 이름을 지정할 수 있습니다.- 네트워크 추적에서 패킷을 캡처하는 동안 네트워크 통신 문제를 트리거하는 웹 애플리케이션 액세스와 같은 작업을 수행합니다.
oc adm must-gather가 Pod에서 클라이언트 머신으로 전송된 패킷 캡처 파일을 확인합니다.tmp/captures ├── event-filter.html ├── ip-10-0-192-217-ec2-internal 1 │ └── registry-redhat-io-openshift4-network-tools-rhel8-sha256-bca... │ └── 2022-01-13T19:31:31.pcap ├── ip-10-0-201-178-ec2-internal 2 │ └── registry-redhat-io-openshift4-network-tools-rhel8-sha256-bca... │ └── 2022-01-13T19:31:30.pcap ├── ip-... └── timestamp
5.5.2. AWS 노드 또는 컨테이너의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 네트워크 추적 수집
AWS에서 잠재적인 네트워크 관련 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 조사할 때 Red Hat 지원은 AWS 클러스터 노드의 특정 Red Hat OpenShift Service 또는 특정 컨테이너에서 네트워크 패킷 추적을 요청할 수 있습니다. AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 네트워크 추적을 캡처하는 데 권장되는 방법은 디버그 Pod를 사용하는 것입니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. - 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스 ID가 있습니다.
프로세스
클러스터 노드 목록을 가져옵니다.
$ oc get nodes
대상 노드에서 디버그 세션으로 들어갑니다. 이 단계는
<node_name>-debug라는 디버그 Pod를 인스턴스화합니다.$ oc debug node/my-cluster-node
디버그 쉘 내에서
/host를 root 디렉터리로 설정합니다. 디버그 Pod는 Pod 내의/host에 호스트의 루트 파일 시스템을 마운트합니다. root 디렉토리를/host로 변경하면 호스트의 실행 경로에 포함된 바이너리를 실행할 수 있습니다.# chroot /host
chroot환경 콘솔에서 노드의 인터페이스 이름을 가져옵니다.# ip ad
sosreport를 실행하는 데 필요한 바이너리 및 플러그인이 포함된toolbox컨테이너를 시작합니다.# toolbox
참고기존
toolboxPod가 이미 실행 중인 경우toolbox명령은'toolbox-' already exists를 출력합니다. Trying to start…를 출력합니다.tcpdump문제를 방지하려면podman rm toolbox-에서 실행중인 toolbox 컨테이너를 제거하고 새 toolbox 컨테이너를 생성합니다.클러스터 노드에서
tcpdump세션을 시작하고 출력을 캡처 파일로 리디렉션합니다. 이 예에서는ens5를 인터페이스 이름으로 사용합니다.$ tcpdump -nn -s 0 -i ens5 -w /host/var/tmp/my-cluster-node_$(date +%d_%m_%Y-%H_%M_%S-%Z).pcap 1- 1
- toolbox 컨테이너가 호스트의 root 디렉토리를
/host에 마운트하기 때문에tcpdump캡처 파일의 경로는chroot환경 외부에 있습니다.
노드의 특정 컨테이너에
tcpdump캡처가 필요한 경우 다음 단계를 따르십시오.대상 컨테이너 ID를 확인합니다. toolbox 컨테이너가 호스트의 root 디렉토리를
/host에 마운트하기 때문에chroot host명령은 이 단계에서crictl명령 보다 우선합니다.# chroot /host crictl ps
컨테이너의 프로세스 ID를 확인합니다. 이 예에서 컨테이너 ID는
a7fe32346b120입니다.# chroot /host crictl inspect --output yaml a7fe32346b120 | grep 'pid' | awk '{print $2}'컨테이너에서
tcpdump세션을 시작하고 출력을 캡처 파일로 리디렉션합니다. 이 예는 컨테이너의 프로세스 ID로49,628을 사용하고 인터페이스 이름으로ens5를 사용합니다.nsenter명령은 대상 프로세스의 네임 스페이스를 입력하고 해당 네임 스페이스를 사용하여 명령을 실행합니다. 이 예에서 대상 프로세스는 컨테이너의 프로세스 ID이므로tcpdump명령은 호스트에서 컨테이너 네임 스페이스를 사용하여 실행됩니다.# nsenter -n -t 49628 -- tcpdump -nn -i ens5 -w /host/var/tmp/my-cluster-node-my-container_$(date +%d_%m_%Y-%H_%M_%S-%Z).pcap 1- 1
- toolbox 컨테이너가 호스트의 root 디렉토리를
/host에 마운트하기 때문에tcpdump캡처 파일의 경로는chroot환경 외부에 있습니다.
분석을 위해 다음 방법 중 하나를 사용하여
tcpdump캡처 파일을 Red Hat 지원팀에 제공합니다.AWS 클러스터의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 직접 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 파일을 업로드합니다.
toolbox 컨테이너 내에서
redhat-support-tool을 실행하여 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 직접 파일을 첨부합니다. 이 예에서는 지원 사례 ID01234567을 사용합니다.# redhat-support-tool addattachment -c 01234567 /host/var/tmp/my-tcpdump-capture-file.pcap 1- 1
- toolbox 컨테이너는
/host에 호스트의 root 디렉토리를 마운트합니다.redhat-support-tool명령에 업로드할 파일을 지정할 때/host/를 포함하여 toolbox 컨테이너의 root 디렉토리에서 절대 경로를 참조합니다.
기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 파일을 업로드합니다.
oc debug node/<node_name>명령을 실행하여sosreport아카이브를 연결하고 출력을 파일로 리디렉션합니다. 이 명령은 이전oc debug세션을 종료했다고 가정합니다.$ oc debug node/my-cluster-node -- bash -c 'cat /host/var/tmp/my-tcpdump-capture-file.pcap' > /tmp/my-tcpdump-capture-file.pcap 1- 1
- 디버그 컨테이너는
/host에 호스트의 root 디렉토리를 마운트합니다. 연결할 대상 파일을 지정할 때/host를 포함하여 디버그 컨테이너의 root 디렉토리에서 절대 경로를 참조합니다.
- Red Hat 고객 포털 의 고객 지원 페이지에서 기존 지원 케이스로 이동합니다.
- Attach files를 선택하고 메시지에 따라 파일을 업로드합니다.
5.5.3. Red Hat 지원에 진단 데이터 제공
AWS에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 조사할 때 Red Hat 지원팀에서 지원 케이스에 진단 데이터를 업로드하도록 요청할 수 있습니다. 파일은 Red Hat Customer Portal을 통해 지원 케이스에 업로드하거나 redhat-support-tool 명령을 사용하여 AWS 클러스터의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 직접 업로드할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
cluster-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있어야 합니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. - 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스 ID가 있습니다.
프로세스
Red Hat 고객 포털을 통해 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 진단 데이터를 업로드합니다.
oc debug node/<node_name> 명령을 사용하여 AWS 노드의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 포함된 진단 파일을 연결하고 출력을 파일로 리디렉션합니다. 다음 예에서는/host/var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz를 디버그 컨테이너에서/var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz로 복사합니다.$ oc debug node/my-cluster-node -- bash -c 'cat /host/var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz' > /var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz 1- 1
- 디버그 컨테이너는
/host에 호스트의 root 디렉토리를 마운트합니다. 연결할 대상 파일을 지정할 때/host를 포함하여 디버그 컨테이너의 root 디렉토리에서 절대 경로를 참조합니다.
- Red Hat 고객 포털 의 고객 지원 페이지에서 기존 지원 케이스로 이동합니다.
- Attach files를 선택하고 메시지에 따라 파일을 업로드합니다.
AWS 클러스터의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 직접 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 진단 데이터를 업로드합니다.
클러스터 노드 목록을 가져옵니다.
$ oc get nodes
대상 노드에서 디버그 세션으로 들어갑니다. 이 단계는
<node_name>-debug라는 디버그 Pod를 인스턴스화합니다.$ oc debug node/my-cluster-node
디버그 쉘 내에서
/host를 root 디렉터리로 설정합니다. 디버그 Pod는 Pod 내의/host에 호스트의 루트 파일 시스템을 마운트합니다. root 디렉토리를/host로 변경하면 호스트의 실행 경로에 포함된 바이너리를 실행할 수 있습니다.# chroot /host
redhat-support-tool을 실행하는 데 필요한 바이너리가 포함된toolbox컨테이너를 시작합니다.# toolbox
참고기존
toolboxPod가 이미 실행 중인 경우toolbox명령은'toolbox-' already exists를 출력합니다. Trying to start…를 출력합니다.podman rm toolbox-에서 실행중인 toolbox 컨테이너를 제거하고 새 toolbox 컨테이너를 생성하여 문제를 방지합니다.redhat-support-tool을 실행하여 디버그 Pod의 파일을 기존 Red Hat 지원 케이스에 직접 첨부합니다. 이 예에서는 지원 케이스 ID '01234567'과 예제 파일 경로/host/var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz를 사용합니다.# redhat-support-tool addattachment -c 01234567 /host/var/tmp/my-diagnostic-data.tar.gz 1- 1
- toolbox 컨테이너는
/host에 호스트의 root 디렉토리를 마운트합니다.redhat-support-tool명령에 업로드할 파일을 지정할 때/host/를 포함하여 toolbox 컨테이너의 root 디렉토리에서 절대 경로를 참조합니다.
5.5.4. toolbox정보
toolbox는 RHCOS(Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS) 시스템에서 컨테이너를 시작하는 툴입니다. 이 툴은 주로 sosreport 및 redhat-support-tool 과 같은 명령을 실행하는 데 필요한 필수 바이너리 및 플러그인이 포함된 컨테이너를 시작하는 데 사용됩니다.
toolbox 컨테이너의 주요 목적은 진단 정보를 수집하여 Red Hat 지원에 제공하는 것입니다. 그러나 추가 진단 도구가 필요한 경우 RPM 패키지를 추가하거나 표준 지원 도구 이미지의 대체 이미지를 실행할 수 있습니다.
toolbox 컨테이너에 패키지 설치
기본적으로 toolbox 명령을 실행하면 registry.redhat.io/rhel8/support-tools:latest 이미지로 컨테이너를 시작합니다. 이 이미지에는 가장 자주 사용되는 지원 도구가 포함되어 있습니다. 이미지에 포함되지 않은 지원 툴이 필요한 노드별 데이터를 수집해야 하는 경우 추가 패키지를 설치할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
oc debug node/<node_name>명령이 있는 노드에 액세스하고 있습니다.
프로세스
디버그 쉘 내에서
/host를 root 디렉터리로 설정합니다. 디버그 Pod는 Pod 내의/host에 호스트의 루트 파일 시스템을 마운트합니다. root 디렉토리를/host로 변경하면 호스트의 실행 경로에 포함된 바이너리를 실행할 수 있습니다.# chroot /host
toolbox 컨테이너를 시작합니다.
# toolbox
wget과 같은 추가 패키지를 설치합니다.# dnf install -y <package_name>
toolbox를 사용하여 대체 이미지 시작
기본적으로 toolbox 명령을 실행하면 registry.redhat.io/rhel8/support-tools:latest 이미지로 컨테이너를 시작합니다. .toolboxrc 파일을 생성하고 실행할 이미지를 지정하여 대체 이미지를 시작할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
oc debug node/<node_name>명령이 있는 노드에 액세스하고 있습니다.
프로세스
디버그 쉘 내에서
/host를 root 디렉터리로 설정합니다. 디버그 Pod는 Pod 내의/host에 호스트의 루트 파일 시스템을 마운트합니다. root 디렉토리를/host로 변경하면 호스트의 실행 경로에 포함된 바이너리를 실행할 수 있습니다.# chroot /host
root 사용자 ID에 대한 홈 디렉터리에
.toolboxrc파일을 생성합니다.# vi ~/.toolboxrc
REGISTRY=quay.io 1 IMAGE=fedora/fedora:33-x86_64 2 TOOLBOX_NAME=toolbox-fedora-33 3
대체 이미지를 사용하여 toolbox 컨테이너를 시작합니다.
# toolbox
참고기존
toolboxPod가 이미 실행 중인 경우toolbox명령은'toolbox-' already exists를 출력합니다. Trying to start…를 출력합니다.podman rm toolbox-에서 실행중인 toolbox 컨테이너를 제거하고 새 toolbox 컨테이너를 생성하여sosreport플러그인 문제를 방지합니다.
6장. 클러스터 사양 요약
6.1. 클러스터 버전 오브젝트를 사용하여 클러스터 사양 요약
clusterversion 리소스를 쿼리하여 AWS 클러스터 사양에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 요약을 가져올 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
클러스터 버전, 가용성, 가동 시간 및 일반 상태를 쿼리합니다.
$ oc get clusterversion
출력 예
NAME VERSION AVAILABLE PROGRESSING SINCE STATUS version 4.13.8 True False 8h Cluster version is 4.13.8
클러스터 사양, 업데이트 가용성 및 업데이트 기록에 대한 자세한 요약을 가져옵니다.
$ oc describe clusterversion
출력 예
Name: version Namespace: Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> API Version: config.openshift.io/v1 Kind: ClusterVersion # ... Image: quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release@sha256:a956488d295fe5a59c8663a4d9992b9b5d0950f510a7387dbbfb8d20fc5970ce URL: https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2023:4456 Version: 4.13.8 History: Completion Time: 2023-08-17T13:20:21Z Image: quay.io/openshift-release-dev/ocp-release@sha256:a956488d295fe5a59c8663a4d9992b9b5d0950f510a7387dbbfb8d20fc5970ce Started Time: 2023-08-17T12:59:45Z State: Completed Verified: false Version: 4.13.8 # ...
7장. 문제 해결
7.1. AWS 설치에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service 문제 해결
7.1.1. 설치 문제 해결
7.1.1.1. 로그 설치 또는 제거 검사
설치 로그를 표시하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
다음 명령을 실행하여 <
cluster_name>을 클러스터 이름으로 교체합니다.$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name>
로그를 조사하려면
--watch플래그를 포함합니다.$ rosa logs install --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
설치 제거 로그를 표시하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
다음 명령을 실행하여 <
cluster_name>을 클러스터 이름으로 교체합니다.$ rosa logs uninstall --cluster=<cluster_name>
로그를 조사하려면
--watch플래그를 포함합니다.$ rosa logs uninstall --cluster=<cluster_name> --watch
7.1.1.2. STS 없이 클러스터에 대한 AWS 계정 권한 확인
다음 명령을 실행하여 AWS 계정에 올바른 권한이 있는지 확인합니다. 이 명령은 AWS STS(Security Token Service)를 사용하지 않는 클러스터에 대해서만 권한을 확인합니다.
$ rosa verify permissions
오류가 발생하면 SCP보다 SCP 가 AWS 계정에 적용되지 않았는지 다시 확인하십시오. SCP를 사용해야 하는 경우 필요한 최소 SCP에 대한 자세한 내용은 Red Hat Requirements for Customer Cloud Subscription 을 참조하십시오.
7.1.1.3. AWS 계정 및 할당량 확인
다음 명령을 실행하여 AWS 계정에서 사용 가능한 할당량이 있는지 확인합니다.
$ rosa verify quota
리전에 따라 AWS 할당량이 변경됩니다. 올바른 AWS 리전에 대한 할당량을 확인하고 있는지 확인합니다. 할당량을 늘려야 하는 경우 AWS 콘솔 로 이동하여 실패한 서비스에 대한 할당량 증가를 요청합니다.
7.1.1.4. AWS 알림 이메일
클러스터를 생성할 때 AWS 서비스의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 지원되는 모든 리전에 작은 인스턴스를 생성합니다. 이렇게 하면 사용 중인 AWS 계정이 지원되는 각 리전에 배포할 수 있습니다.
지원되는 모든 리전을 사용하지 않는 AWS 계정의 경우 AWS는 "Your Request For Accessing AWS Resources Has Been Validated"를 확인하도록 하나 이상의 이메일을 보낼 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 이 이메일의 발신자는 aws-verification@amazon.com 입니다.
이는 AWS 서비스의 Red Hat OpenShift Service가 AWS 계정 구성을 검증하고 있기 때문에 예상되는 동작입니다.
7.2. 네트워킹 문제 해결
이 문서에서는 네트워킹 오류 문제를 해결하는 방법을 설명합니다.
7.2.1. 프라이빗 네트워크 로드 밸런서가 있는 클러스터의 연결 문제
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service 및 버전 4로 생성된 HCP 클러스터를 사용하는 ROSA는 기본적으로 기본 수신 컨트롤러에 대해 AWS NLB(Network Load Balancer)를 배포합니다. 개인 NLB의 경우 NLB의 클라이언트 IP 주소 보존으로 인해 소스와 대상이 동일한 호스트인 연결이 삭제될 수 있습니다. Network Load Balancer 문제 해결 방법에 대한 AWS 설명서를 참조하십시오. 이 IP 주소 보존은 모든 고객 워크로드가 라우터 Pod와 동일한 노드에서 충돌 컨트롤러 라우터 앞의 개인 NLB로 트래픽을 보낼 수 없다는 것을 의미합니다.
이러한 영향을 완화하려면 고객의 워크로드를 라우터 Pod가 예약된 노드와 별도로 다시 예약해야 합니다. 또는 고객은 동일한 클러스터 내에서 공동 배치된 다른 워크로드에 액세스하기 위해 내부 Pod 및 서비스 네트워크를 사용해야 합니다.
7.3. 노드 상태 확인
7.3.1. 노드 상태, 리소스 사용량 및 구성 확인
클러스터 노드 상태, 리소스 사용량 통계 및 노드 로그를 확인합니다. 또한 개별 노드에서 kubelet 상태를 쿼리합니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
클러스터의 모든 노드 이름, 상태 및 역할을 나열합니다.
$ oc get nodes
클러스터 내의 각 노드에 대한 CPU 및 메모리 사용량을 요약합니다.
$ oc adm top nodes
특정 노드의 CPU 및 메모리 사용량을 요약합니다.
$ oc adm top node my-node
7.4. Operator 문제 해결
Operator는 AWS 애플리케이션에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 패키징, 배포 및 관리하는 방법입니다. 소프트웨어 벤더 엔지니어링 팀의 확장 기능으로, AWS 환경에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 감시하고 현재 상태를 사용하여 실시간으로 의사 결정을 내립니다. Operator는 업그레이드를 원활하게 처리하고 오류 발생에 자동으로 대응하며 시간을 절약하기 위해 소프트웨어 백업 프로세스를 생략하는 것과 같은 바로가기를 실행하지 않습니다.
AWS 4의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에는 클러스터가 제대로 작동하는 데 필요한 기본 Operator 세트가 포함되어 있습니다. 이러한 기본 운영자는 CVO (Cluster Version Operator)에 의해 관리됩니다.
클러스터 관리자는 AWS 웹 콘솔 또는 CLI의 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 사용하여 OperatorHub에서 애플리케이션 Operator를 설치할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 Operator를 하나 이상의 네임 스페이스에 가입시켜 클러스터의 개발자가 사용할 수 있도록합니다. 애플리케이션 Operator는 OLM (Operator Lifecycle Manager)에서 관리합니다.
Operator 문제가 발생하면 Operator 서브스크립션 상태를 확인하십시오. 클러스터 전체에서 Operator Pod 상태를 확인하고 진단을 위해 Operator 로그를 수집합니다.
7.4.1. Operator 서브스크립션 상태 유형
서브스크립션은 다음 상태 유형을 보고할 수 있습니다.
표 7.1. 서브스크립션 상태 유형
| 상태 | 설명 |
|---|---|
|
| 해결에 사용되는 일부 또는 모든 카탈로그 소스가 정상 상태가 아닙니다. |
|
| 서브스크립션 설치 계획이 없습니다. |
|
| 서브스크립션 설치 계획이 설치 대기 중입니다. |
|
| 서브스크립션 설치 계획이 실패했습니다. |
|
| 서브스크립션의 종속성 확인에 실패했습니다. |
AWS 클러스터 Operator의 기본 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 CVO(Cluster Version Operator)에 의해 관리되며 Subscription 오브젝트가 없습니다. 애플리케이션 Operator는 OLM(Operator Lifecycle Manager)에서 관리하며 Subscription 오브젝트가 있습니다.
추가 리소스
7.4.2. CLI를 사용하여 Operator 서브스크립션 상태 보기
CLI를 사용하여 Operator 서브스크립션 상태를 볼 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
Operator 서브스크립션을 나열합니다.
$ oc get subs -n <operator_namespace>
oc describe명령을 사용하여Subscription리소스를 검사합니다.$ oc describe sub <subscription_name> -n <operator_namespace>
명령 출력에서 Operator 서브스크립션 조건 유형의 상태에 대한
Conditions섹션을 확인합니다. 다음 예에서 사용 가능한 모든 카탈로그 소스가 정상이므로CatalogSourcesUnhealthy조건 유형의 상태가false입니다.출력 예
Name: cluster-logging Namespace: openshift-logging Labels: operators.coreos.com/cluster-logging.openshift-logging= Annotations: <none> API Version: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 Kind: Subscription # ... Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2019-07-29T13:42:57Z Message: all available catalogsources are healthy Reason: AllCatalogSourcesHealthy Status: False Type: CatalogSourcesUnhealthy # ...
AWS 클러스터 Operator의 기본 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 CVO(Cluster Version Operator)에 의해 관리되며 Subscription 오브젝트가 없습니다. 애플리케이션 Operator는 OLM(Operator Lifecycle Manager)에서 관리하며 Subscription 오브젝트가 있습니다.
7.4.3. CLI를 사용하여 Operator 카탈로그 소스 상태 보기
CLI를 사용하여 Operator 카탈로그 소스의 상태를 볼 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
네임스페이스의 카탈로그 소스를 나열합니다. 예를 들어 클러스터 전체 카탈로그 소스에 사용되는
openshift-marketplace네임스페이스를 확인할 수 있습니다.$ oc get catalogsources -n openshift-marketplace
출력 예
NAME DISPLAY TYPE PUBLISHER AGE certified-operators Certified Operators grpc Red Hat 55m community-operators Community Operators grpc Red Hat 55m example-catalog Example Catalog grpc Example Org 2m25s redhat-marketplace Red Hat Marketplace grpc Red Hat 55m redhat-operators Red Hat Operators grpc Red Hat 55m
oc describe명령을 사용하여 카탈로그 소스에 대한 자세한 내용 및 상태를 가져옵니다.$ oc describe catalogsource example-catalog -n openshift-marketplace
출력 예
Name: example-catalog Namespace: openshift-marketplace Labels: <none> Annotations: operatorframework.io/managed-by: marketplace-operator target.workload.openshift.io/management: {"effect": "PreferredDuringScheduling"} API Version: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1 Kind: CatalogSource # ... Status: Connection State: Address: example-catalog.openshift-marketplace.svc:50051 Last Connect: 2021-09-09T17:07:35Z Last Observed State: TRANSIENT_FAILURE Registry Service: Created At: 2021-09-09T17:05:45Z Port: 50051 Protocol: grpc Service Name: example-catalog Service Namespace: openshift-marketplace # ...앞의 예제 출력에서 마지막으로 관찰된 상태는
TRANSIENT_FAILURE입니다. 이 상태는 카탈로그 소스에 대한 연결을 설정하는 데 문제가 있음을 나타냅니다.카탈로그 소스가 생성된 네임스페이스의 Pod를 나열합니다.
$ oc get pods -n openshift-marketplace
출력 예
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE certified-operators-cv9nn 1/1 Running 0 36m community-operators-6v8lp 1/1 Running 0 36m marketplace-operator-86bfc75f9b-jkgbc 1/1 Running 0 42m example-catalog-bwt8z 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 3m55s redhat-marketplace-57p8c 1/1 Running 0 36m redhat-operators-smxx8 1/1 Running 0 36m
카탈로그 소스가 네임스페이스에 생성되면 해당 네임스페이스에 카탈로그 소스의 Pod가 생성됩니다. 위 예제 출력에서
example-catalog-bwt8zpod의 상태는ImagePullBackOff입니다. 이 상태는 카탈로그 소스의 인덱스 이미지를 가져오는 데 문제가 있음을 나타냅니다.자세한 정보는
oc describe명령을 사용하여 Pod를 검사합니다.$ oc describe pod example-catalog-bwt8z -n openshift-marketplace
출력 예
Name: example-catalog-bwt8z Namespace: openshift-marketplace Priority: 0 Node: ci-ln-jyryyg2-f76d1-ggdbq-worker-b-vsxjd/10.0.128.2 ... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal Scheduled 48s default-scheduler Successfully assigned openshift-marketplace/example-catalog-bwt8z to ci-ln-jyryyf2-f76d1-fgdbq-worker-b-vsxjd Normal AddedInterface 47s multus Add eth0 [10.131.0.40/23] from openshift-sdn Normal BackOff 20s (x2 over 46s) kubelet Back-off pulling image "quay.io/example-org/example-catalog:v1" Warning Failed 20s (x2 over 46s) kubelet Error: ImagePullBackOff Normal Pulling 8s (x3 over 47s) kubelet Pulling image "quay.io/example-org/example-catalog:v1" Warning Failed 8s (x3 over 47s) kubelet Failed to pull image "quay.io/example-org/example-catalog:v1": rpc error: code = Unknown desc = reading manifest v1 in quay.io/example-org/example-catalog: unauthorized: access to the requested resource is not authorized Warning Failed 8s (x3 over 47s) kubelet Error: ErrImagePull
앞의 예제 출력에서 오류 메시지는 권한 부여 문제로 인해 카탈로그 소스의 인덱스 이미지를 성공적으로 가져오지 못한 것으로 표시됩니다. 예를 들어 인덱스 이미지는 로그인 인증 정보가 필요한 레지스트리에 저장할 수 있습니다.
추가 리소스
- gRPC 문서: 연결 상태
7.4.4. Operator Pod 상태 쿼리
클러스터 내의 Operator Pod 및 해당 상태를 나열할 수 있습니다. 자세한 Operator Pod 요약을 수집할 수도 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
클러스터에서 실행중인 Operator를 나열합니다. 출력에는 Operator 버전, 가용성 및 가동 시간 정보가 포함됩니다.
$ oc get clusteroperators
Operator의 네임스페이스에서 실행 중인 Operator Pod와 Pod 상태, 재시작, 경과 시간을 표시합니다.
$ oc get pod -n <operator_namespace>
자세한 Operator Pod 요약을 출력합니다.
$ oc describe pod <operator_pod_name> -n <operator_namespace>
7.4.5. Operator 로그 수집
Operator 문제가 발생하면 Operator Pod 로그에서 자세한 진단 정보를 수집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. - 컨트롤 플레인 또는 컨트롤 플레인 시스템의 정규화된 도메인 이름이 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
Operator의 네임스페이스에서 실행 중인 Operator Pod와 Pod 상태, 재시작, 경과 시간을 표시합니다.
$ oc get pods -n <operator_namespace>
Operator Pod의 로그를 검토합니다.
$ oc logs pod/<pod_name> -n <operator_namespace>
Operator Pod에 컨테이너가 여러 개 있는 경우 위 명령에 의해 각 컨테이너의 이름이 포함된 오류가 생성됩니다. 개별 컨테이너의 로그를 쿼리합니다.
$ oc logs pod/<operator_pod_name> -c <container_name> -n <operator_namespace>
API가 작동하지 않는 경우 대신 SSH를 사용하여 각 컨트롤 플레인 노드에서 Operator Pod 및 컨테이너 로그를 검토합니다.
<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>을 적절한 값으로 바꿉니다.각 컨트롤 플레인 노드에 Pod를 나열합니다.
$ ssh core@<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> sudo crictl pods
Ready상태가 표시되지 않는 Operator Pod의 경우 Pod 상태를 자세히 검사합니다.<operator_pod_id>를 이전 명령의 출력에 나열된 Operator Pod의 ID로 교체합니다.$ ssh core@<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> sudo crictl inspectp <operator_pod_id>
Operator Pod와 관련된 컨테이너를 나열합니다.
$ ssh core@<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> sudo crictl ps --pod=<operator_pod_id>
Ready상태가 표시되지 않는 Operator 컨테이너의 경우 컨테이너 상태를 자세히 검사합니다.<container_id>를 이전 명령의 출력에 나열된 컨테이너 ID로 바꿉니다.$ ssh core@<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> sudo crictl inspect <container_id>
Ready상태가 표시되지 않는 Operator 컨테이너의 로그를 확인합니다.<container_id>를 이전 명령의 출력에 나열된 컨테이너 ID로 바꿉니다.$ ssh core@<master-node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain> sudo crictl logs -f <container_id>
참고RHCOS(Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS)를 실행하는 AWS 4 클러스터 노드의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 변경할 수 없으며 Operator를 통해 클러스터 변경 사항을 적용합니다. SSH를 사용하여 클러스터 노드에 액세스하는 것은 권장되지 않습니다. SSH를 통해 진단 데이터를 수집하기 전에
oc adm must gather및 기타oc명령을 실행하여 충분한 데이터를 수집할 수 있는지 확인하십시오. 그러나 AWS API의 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 사용할 수 없거나 kubelet이 대상 노드에서 제대로 작동하지 않는 경우oc작업이 영향을 받습니다. 이러한 상황에서ssh core@<node>.<cluster_name>.<base_domain>을 사용하여 노드에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
7.5. Pod 문제 조사
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS는 하나의 호스트에 함께 배포되는 하나 이상의 컨테이너인 Pod의 Kubernetes 개념을 활용합니다. Pod는 AWS 4의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 정의, 배포 및 관리할 수 있는 최소 컴퓨팅 단위입니다.
Pod가 정의되면 컨테이너가 종료될 때까지 또는 제거될 때까지 노드에서 실행되도록 할당됩니다. 정책 및 종료 코드에 따라 Pod는 종료 후 제거되거나 해당 로그에 액세스할 수 있도록 유지됩니다.
Pod 문제 발생 시 가장 먼저 Pod의 상태를 확인합니다. Pod의 명시적인 오류가 발생한 경우에는 Pod의 오류 상태를 확인하여 특정 이미지, 컨테이너 또는 Pod 네트워크 문제를 파악합니다. 오류 상태에 따라 진단 데이터를 수집합니다. Pod 이벤트 메시지와 Pod 및 컨테이너 로그 정보를 확인합니다. 명령줄에서 실행 중인 Pod에 액세스하여 문제를 동적으로 진단하거나 문제가 있는 Pod의 배포 구성을 기반으로 루트 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
7.5.1. Pod 오류 상태 이해
Pod에서 오류가 발생하면 명시적 오류 상태를 반환하며 oc get Pods 출력의 status 필드에서 확인할 수 있습니다. Pod 오류 상태에는 이미지, 컨테이너 및 컨테이너 네트워크 관련 오류가 포함됩니다.
다음 표에는 Pod 오류 상태 및 설명이 기재되어 있습니다.
표 7.2. Pod 오류 상태
| Pod 오류 상태 | 설명 |
|---|---|
|
| 일반 이미지 검색 오류입니다. |
|
| 이미지 검색에 실패하여 백 오프되었습니다. |
|
| 지정된 이미지 이름이 잘못되었습니다. |
|
| 이미지 검사에 실패했습니다. |
|
|
|
|
| 레지스트리에서 이미지 검색을 시도할 때 HTTP 오류가 발생했습니다. |
|
| 지정된 컨테이너가 선언된 Pod에 존재하지 않거나 kubelet에 의해 관리되지 않습니다. |
|
| 컨테이너 초기화에 실패했습니다. |
|
| Pod의 컨테이너가 정상적으로 시작되지 않았습니다. |
|
| Pod의 컨테이너가 정상적으로 종료되지 않았습니다. |
|
| 컨테이너가 종료되었습니다. kubelet은 재시작을 시도하지 않습니다. |
|
| 컨테이너 또는 이미지가 root 권한으로 실행하려고 했습니다. |
|
| Pod 샌드 박스 생성에 실패했습니다. |
|
| Pod 샌드 박스 구성을 가져오지 못했습니다. |
|
| Pod의 샌드박스가 정상적으로 중지되지 않았습니다. |
|
| 네트워크 초기화에 실패했습니다. |
|
| 네트워크 종료에 실패했습니다. |
7.5.2. Pod 상태 검토
Pod 상태 및 오류 상태를 쿼리할 수 있습니다. Pod의 관련 배포 구성을 쿼리하고 기본 이미지 가용성을 검토할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. -
skopeo가 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
프로젝트로 전환합니다.
$ oc project <project_name>
네임스페이스 내에서 실행 중인 Pod와 Pod 상태, 오류 상태, 재시작, 경과 시간을 표시합니다.
$ oc get pods
네임 스페이스가 배포 구성에 의해 관리되는지 확인합니다.
$ oc status
네임 스페이스가 배포 구성으로 관리되는 경우 출력에 배포 구성 이름과 기본 이미지 참조가 포함됩니다.
이전 명령의 출력에서 참조되는 기본 이미지를 검사합니다.
$ skopeo inspect docker://<image_reference>
기본 이미지 참조가 올바르지 않으면 배치 구성에서 참조를 업데이트합니다.
$ oc edit deployment/my-deployment
배포 구성이 완료된 후 변경되면 구성이 자동으로 다시 배포됩니다. 배포가 진행되는 동안 Pod 상태를 확인하여 문제가 해결되었는지 확인합니다.
$ oc get pods -w
Pod 실패와 관련된 진단 정보를 보려면 네임스페이스 내의 이벤트를 검토합니다.
$ oc get events
7.5.3. Pod 및 컨테이너 로그 검사
Pod 및 컨테이너 로그에서 명시적 Pod 실패와 관련된 경고 및 오류 메시지를 검사할 수 있습니다. 정책 및 종료 코드에 따라 Pod가 종료된 후에도 Pod 및 컨테이너 로그를 계속 사용할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
특정 Pod의 로그를 쿼리합니다.
$ oc logs <pod_name>
Pod에서 특정 컨테이너의 로그를 쿼리합니다.
$ oc logs <pod_name> -c <container_name>
이전
oc logs명령을 사용하여 검색된 로그는 Pod 또는 컨테이너 내에서 stdout으로 전송된 메시지로 구성됩니다.Pod에서
/var/log/에 포함된 로그를 검사합니다.Pod에서
/var/log에 포함된 로그 파일 및 하위 디렉터리를 나열합니다.$ oc exec <pod_name> -- ls -alh /var/log
출력 예
total 124K drwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 33 Aug 11 11:23 . drwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 28 Sep 6 2022 .. -rw-rw----. 1 root utmp 0 Jul 10 10:31 btmp -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 33K Jul 17 10:07 dnf.librepo.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 69K Jul 17 10:07 dnf.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8.8K Jul 17 10:07 dnf.rpm.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 480 Jul 17 10:07 hawkey.log -rw-rw-r--. 1 root utmp 0 Jul 10 10:31 lastlog drwx------. 2 root root 23 Aug 11 11:14 openshift-apiserver drwx------. 2 root root 6 Jul 10 10:31 private drwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 22 Mar 9 08:05 rhsm -rw-rw-r--. 1 root utmp 0 Jul 10 10:31 wtmp
Pod에서
/var/log에 포함된 특정 로그 파일을 쿼리합니다.$ oc exec <pod_name> cat /var/log/<path_to_log>
출력 예
2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 INFO --- logging initialized --- 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 DDEBUG timer: config: 13 ms 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 DEBUG Loaded plugins: builddep, changelog, config-manager, copr, debug, debuginfo-install, download, generate_completion_cache, groups-manager, needs-restarting, playground, product-id, repoclosure, repodiff, repograph, repomanage, reposync, subscription-manager, uploadprofile 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 INFO Updating Subscription Management repositories. 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 INFO Unable to read consumer identity 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 INFO Subscription Manager is operating in container mode. 2023-07-10T10:29:38+0000 INFO
특정 컨테이너의
/var/log에 포함된 로그 파일 및 하위 디렉토리를 나열합니다.$ oc exec <pod_name> -c <container_name> ls /var/log
특정 컨테이너의
/var/log에 포함된 특정 로그 파일을 쿼리합니다.$ oc exec <pod_name> -c <container_name> cat /var/log/<path_to_log>
7.5.4. 실행 중인 Pod에 액세스
Pod 내에서 쉘을 열거나 포트 전달을 통해 네트워크 액세스 권한을 취득하여 실행 중인 Pod를 동적으로 확인할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
액세스하려는 Pod가 포함된 프로젝트로 전환합니다. 이는
oc rsh명령이-nnamespace 옵션을 허용하지 않기 때문에 필요합니다.$ oc project <namespace>
Pod에서 원격 쉘을 시작합니다.
$ oc rsh <pod_name> 1- 1
- Pod에 컨테이너가 여러 개 있는 경우
-c <container_name>을 지정하지 않으면oc rsh는 첫 번째 컨테이너로 기본 설정됩니다.
Pod에서 특정 컨테이너로 원격 쉘을 시작합니다.
$ oc rsh -c <container_name> pod/<pod_name>
Pod에서 포트로의 포트 전달 세션을 만듭니다.
$ oc port-forward <pod_name> <host_port>:<pod_port> 1- 1
Ctrl+C를 입력하여 포트 전달 세션을 취소합니다.
7.5.5. 루트 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod 시작
문제가 있는 Pod 배포 또는 배포 구성에 따라 루트 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작할 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 Pod 사용자는 루트가 아닌 권한으로 실행되지만 임시 루트 권한으로 문제 해결 Pod를 실행하면 문제 해결에 유용할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
배포에 따라 루트 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
프로젝트의 배포 이름을 가져옵니다.
$ oc get deployment -n <project_name>
배포에 따라 루트 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
$ oc debug deployment/my-deployment --as-root -n <project_name>
배포 구성에 따라 루트 액세스 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
프로젝트의 배포 구성 이름을 가져옵니다.
$ oc get deploymentconfigs -n <project_name>
배포 구성에 따라 루트 권한으로 디버그 Pod를 시작합니다.
$ oc debug deploymentconfig/my-deployment-configuration --as-root -n <project_name>
대화형 쉘을 실행하는 대신 -<command>를 이전 oc debug 명령에 추가하여 디버그 Pod 내에서 개별 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다.
7.5.6. Pod 및 컨테이너 간 파일 복사
Pod 간에 파일을 복사하여 구성 변경을 테스트하거나 진단 정보를 수집할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. - API 서비스가 작동하고 있어야 합니다.
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
7.6. 스토리지 문제 해결
7.6.1. 다중 연결 오류 해결
노드가 예기치 않게 중단되거나 종료되면 연결된 RWO(ReadWriteOnce) 볼륨이 노드에서 마운트 해제되어 다른 노드에서 예약된 Pod에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
그러나 오류가 발생한 노드가 연결된 볼륨을 마운트 해제할 수 없기 때문에 새 노드에 마운트할 수 없습니다.
다중 연결 오류가 보고됩니다.
출력 예
Unable to attach or mount volumes: unmounted volumes=[sso-mysql-pvol], unattached volumes=[sso-mysql-pvol default-token-x4rzc]: timed out waiting for the condition Multi-Attach error for volume "pvc-8837384d-69d7-40b2-b2e6-5df86943eef9" Volume is already used by pod(s) sso-mysql-1-ns6b4
프로세스
다중 연결 문제를 해결하려면 다음 해결 방법 중 하나를 사용합니다.
RWX 볼륨을 사용하여 여러 연결을 활성화합니다.
대부분의 스토리지 솔루션의 경우 RWX (ReadWriteMany) 볼륨을 사용하여 다중 연결 오류를 방지할 수 있습니다.
RWO 볼륨을 사용할 때 오류가 발생한 노드를 복구하거나 삭제합니다.
VMware vSphere와 같이 RWX를 지원하지 않는 스토리지의 경우 RWO 볼륨을 대신 사용해야합니다. 그러나 RWO 볼륨은 여러 노드에 마운트할 수 없습니다.
RWO 볼륨에 다중 연결 오류 메시지가 표시되면 종료되거나 충돌한 노드에서 pod를 강제로 삭제하여 동적 영구 볼륨이 연결된 경우와 같이 중요한 워크로드의 데이터 손실을 방지합니다.
$ oc delete pod <old_pod> --force=true --grace-period=0
이 명령은 종료되거나 중단된 노드에서 멈춘 볼륨을 6분 후 삭제합니다.
7.7. 모니터링 문제 조사
AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에는 핵심 플랫폼 구성 요소를 모니터링할 수 있는 사전 구성, 사전 설치 및 자체 업데이트 모니터링 스택이 포함되어 있습니다. AWS 4의 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 클러스터 관리자는 선택 옵션으로 사용자 정의 프로젝트에 대한 모니터링을 활성화할 수 있습니다.
다음 문제가 발생하는 경우 다음 절차를 사용하십시오.
- 자체 메트릭을 사용할 수 없습니다.
- Prometheus는 많은 디스크 공간을 사용하고 있습니다.
-
Prometheus에서
KubePersistentVolumeFillingUp경고가 실행됩니다.
7.7.1. 사용자 정의 프로젝트 메트릭을 사용할 수 없는 이유 조사
ServiceMonitor 리소스를 사용하면 사용자 정의 프로젝트에서 서비스에 의해 노출되는 메트릭을 사용하는 방법을 확인할 수 있습니다. ServiceMonitor 리소스를 생성했지만 메트릭 UI에서 해당 메트릭을볼 수 없는 경우 이 프로세스에 설명된 단계를 수행하십시오.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다. - 사용자 정의 프로젝트에 대한 모니터링을 활성화 및 구성했습니다.
-
ServiceMonitor리소스가 생성되어 있습니다.
프로세스
서비스 및
ServiceMonitor리소스 구성에서 해당 라벨이 일치하는지 확인합니다.서비스에 정의된 라벨을 가져옵니다. 다음 예제에서는
ns1프로젝트의prometheus-example-app서비스를 쿼리합니다.$ oc -n ns1 get service prometheus-example-app -o yaml
출력 예
labels: app: prometheus-example-appServiceMonitor리소스 구성의matchLabels정의가 이전 단계의 라벨 출력과 일치하는지 확인합니다. 다음 예제에서는ns1프로젝트의prometheus-example-monitor서비스 모니터를 쿼리합니다.$ oc -n ns1 get servicemonitor prometheus-example-monitor -o yaml
출력 예
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceMonitor metadata: name: prometheus-example-monitor namespace: ns1 spec: endpoints: - interval: 30s port: web scheme: http selector: matchLabels: app: prometheus-example-app참고프로젝트 보기 권한이 있는 개발자로서 서비스 및
ServiceMonitor리소스 라벨을 확인할 수 있습니다.
openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트에서 Prometheus Operator의 로그를 검사합니다.openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트의 Pod를 나열합니다.$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring get pods
출력 예
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE prometheus-operator-776fcbbd56-2nbfm 2/2 Running 0 132m prometheus-user-workload-0 5/5 Running 1 132m prometheus-user-workload-1 5/5 Running 1 132m thanos-ruler-user-workload-0 3/3 Running 0 132m thanos-ruler-user-workload-1 3/3 Running 0 132m
prometheus-operatorpod의prometheus-operator컨테이너에서 로그를 가져옵니다. 다음 예에서 Pod는prometheus-operator-776fcbbd56-2nbfm입니다.$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring logs prometheus-operator-776fcbbd56-2nbfm -c prometheus-operator
서비스 모니터에 문제가 있는 경우 로그에 다음과 유사한 오류가 포함될 수 있습니다.
level=warn ts=2020-08-10T11:48:20.906739623Z caller=operator.go:1829 component=prometheusoperator msg="skipping servicemonitor" error="it accesses file system via bearer token file which Prometheus specification prohibits" servicemonitor=eagle/eagle namespace=openshift-user-workload-monitoring prometheus=user-workload
AWS 웹 콘솔 UI의 Red Hat OpenShift Service의 Metrics 대상 페이지에서 끝점의 대상 상태를 확인합니다.
- AWS 웹 콘솔에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service에 로그인하고 관리자 관점에서 모니터링 → 대상으로 이동합니다.
- 목록에서 지표 끝점을 찾고 상태 열에서 대상의 상태를 검토합니다.
- 상태 가 Down 인 경우 끝점의 URL을 클릭하여 해당 지표 대상의 대상 세부 정보 페이지에 대한 자세한 정보를 확인합니다.
openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트에서 Prometheus Operator의 디버그 수준 로깅을 구성합니다.openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트에서user-workload-monitoring-configConfigMap오브젝트를 편집합니다.$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring edit configmap user-workload-monitoring-config
prometheusOperator의logLevel:debug를data / config.yaml아래에 추가하여 로그 수준을debug로 설정합니다.apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: user-workload-monitoring-config namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring data: config.yaml: | prometheusOperator: logLevel: debug # ...파일을 저장하여 변경 사항을 적용합니다.
참고openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트의prometheus-operator는 로그 수준 변경을 적용하면 자동으로 다시 시작됩니다.openshift-user-workload-monitoring프로젝트의prometheus-operator배포에debug로그 수준이 적용되었는지 확인합니다.$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring get deploy prometheus-operator -o yaml | grep "log-level"
출력 예
- --log-level=debug
디버그 수준 로깅은 Prometheus Operator가 수행한 모든 호출을 표시합니다.
prometheus-operatorPod가 실행되고 있는지 확인합니다.$ oc -n openshift-user-workload-monitoring get pods
참고구성 맵에 인식할 수 없는 Prometheus Operator
loglevel값이 포함된 경우prometheus-operatorPod가 재시작되지 않을 수 있습니다.-
디버그 로그를 검토하여 Prometheus Operator에서
ServiceMonitor리소스를 사용하고 있는지 확인합니다. 기타 관련 오류에 대한 로그를 확인합니다.
추가 리소스
7.7.2. Prometheus가 많은 디스크 공간을 소비하는 이유 확인
개발자는 라벨을 생성하여 키-값 쌍의 형식으로 메트릭의 속성을 정의할 수 있습니다. 잠재적인 키-값 쌍의 수는 속성에 사용 가능한 값의 수에 해당합니다. 무제한의 잠재적인 값이 있는 속성을 바인딩되지 않은 속성이라고 합니다. 예를 들어, customer_id 속성은 무제한 가능한 값이 있기 때문에 바인딩되지 않은 속성입니다.
할당된 모든 키-값 쌍에는 고유한 시계열이 있습니다. 라벨에 있는 바인딩되지 않은 많은 속성을 사용하면 생성되는 시계열 수가 기하급수적으로 증가할 수 있습니다. 이는 Prometheus 성능에 영향을 미칠 수 있으며 많은 디스크 공간을 소비할 수 있습니다.
Prometheus가 많은 디스크를 사용하는 경우 다음 조치를 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 가장 많은 시계열 데이터를 생성하는 라벨에 대한 자세한 내용은 Prometheus HTTP API를 사용하여 시계열 데이터베이스(TSDB) 상태를 확인합니다. 이렇게 하려면 클러스터 관리자 권한이 필요합니다.
- 수집 중인 스크랩 샘플 수를 확인합니다.
사용자 정의 메트릭에 할당되는 바인딩되지 않은 속성의 수를 줄임으로써 생성되는 고유의 시계열 수를 감소합니다.
참고사용 가능한 값의 제한된 집합에 바인딩되는 속성을 사용하면 가능한 키 - 값 쌍 조합의 수가 줄어듭니다.
- 사용자 정의 프로젝트에서 스크랩할 수 있는 샘플 수를 제한합니다. 여기에는 클러스터 관리자 권한이 필요합니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
- 관리자 화면에서 모니터링 → 메트릭으로 이동합니다.
Expression 필드에 PromQL(Prometheus Query Language) 쿼리를 입력합니다. 다음 예제 쿼리는 디스크 공간 소비가 증가할 수 있는 높은 카디널리티 메트릭을 식별하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
다음 쿼리를 실행하면 스크랩 샘플 수가 가장 많은 10개의 작업을 확인할 수 있습니다.
topk(10, max by(namespace, job) (topk by(namespace, job) (1, scrape_samples_post_metric_relabeling)))
다음 쿼리를 실행하면 지난 시간에 가장 많은 시계열 데이터를 생성한 10개의 작업을 식별하여 시계열 churn을 정확하게 지정할 수 있습니다.
topk(10, sum by(namespace, job) (sum_over_time(scrape_series_added[1h])))
예상 스크랩 샘플 수보다 많은 메트릭에 할당된 바인딩되지 않은 라벨 값의 수를 조사합니다.
- 메트릭이 사용자 정의 프로젝트와 관련된 경우 워크로드에 할당된 메트릭의 키-값 쌍을 확인합니다. 이는 애플리케이션 수준에서 Prometheus 클라이언트 라이브러리를 통해 구현됩니다. 라벨에서 참조되는 바인딩되지 않은 속성의 수를 제한하십시오.
- 메트릭이 AWS 프로젝트의 핵심 Red Hat OpenShift Service와 관련된 경우 Red Hat 고객 포털에서 Red Hat 지원 케이스를 생성하십시오.
dedicated-admin으로 로그인할 때 다음 단계에 따라 Prometheus HTTP API를 사용하여 TSDB 상태를 확인합니다.다음 명령을 실행하여 Prometheus API 경로 URL을 가져옵니다.
$ HOST=$(oc -n openshift-monitoring get route prometheus-k8s -ojsonpath={.spec.host})다음 명령을 실행하여 인증 토큰을 추출합니다.
$ TOKEN=$(oc whoami -t)
다음 명령을 실행하여 Prometheus의 TSDB 상태를 쿼리합니다.
$ curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -k "https://$HOST/api/v1/status/tsdb"
출력 예
"status": "success","data":{"headStats":{"numSeries":507473, "numLabelPairs":19832,"chunkCount":946298,"minTime":1712253600010, "maxTime":1712257935346},"seriesCountByMetricName": [{"name":"etcd_request_duration_seconds_bucket","value":51840}, {"name":"apiserver_request_sli_duration_seconds_bucket","value":47718}, ...
7.7.3. Prometheus에 대해 KubePersistentVolumeFillingUp 경고가 실행됨
클러스터 관리자는 Prometheus에 대해 KubePersistentVolumeFillingUp 경고가 트리거되는 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
openshift-monitoring 프로젝트의 prometheus-k8s-* Pod에서 클레임한 PV(영구 볼륨)가 남아 있는 총 공간이 3% 미만인 경우 발생합니다. 이로 인해 Prometheus가 비정상적으로 작동할 수 있습니다.
KubePersistentVolumeFillingUp 경고 두 가지가 있습니다.
-
critical alert: mounted PV의 총 공간이 3% 미만이면
severity="critical"라벨이 있는 경고가 트리거됩니다. -
경고 경고: mounted PV의 총 공간이 15 % 미만이고 4 일 이내에 채울 것으로 예상되는 경우
severity="warning"라벨이 있는 경고가 트리거됩니다.
이 문제를 해결하려면 Prometheus TSDB(time-series database) 블록을 제거하여 PV에 더 많은 공간을 생성할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
dedicated-admin역할의 사용자로 클러스터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. -
OpenShift CLI(
oc)가 설치되어 있습니다.
프로세스
다음 명령을 실행하여 가장 오래된 것에서 최신으로 정렬된 모든 TSDB 블록의 크기를 나열합니다.
$ oc debug <prometheus_k8s_pod_name> -n openshift-monitoring \1 -c prometheus --image=$(oc get po -n openshift-monitoring <prometheus_k8s_pod_name> \2 -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[?(@.name=="prometheus")].image}') \ -- sh -c 'cd /prometheus/;du -hs $(ls -dt */ | grep -Eo "[0-9|A-Z]{26}")'
출력 예
308M 01HVKMPKQWZYWS8WVDAYQHNMW6 52M 01HVK64DTDA81799TBR9QDECEZ 102M 01HVK64DS7TRZRWF2756KHST5X 140M 01HVJS59K11FBVAPVY57K88Z11 90M 01HVH2A5Z58SKT810EM6B9AT50 152M 01HV8ZDVQMX41MKCN84S32RRZ1 354M 01HV6Q2N26BK63G4RYTST71FBF 156M 01HV664H9J9Z1FTZD73RD1563E 216M 01HTHXB60A7F239HN7S2TENPNS 104M 01HTHMGRXGS0WXA3WATRXHR36B
제거할 수 있는 블록 수와 블록을 확인한 다음 블록을 제거합니다. 다음 예제 명령은
prometheus-k8s-0Pod에서 가장 오래된 세 가지 Prometheus TSDB 블록을 제거합니다.$ oc debug prometheus-k8s-0 -n openshift-monitoring \ -c prometheus --image=$(oc get po -n openshift-monitoring prometheus-k8s-0 \ -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[?(@.name=="prometheus")].image}') \ -- sh -c 'ls -latr /prometheus/ | egrep -o "[0-9|A-Z]{26}" | head -3 | \ while read BLOCK; do rm -r /prometheus/$BLOCK; done'마운트된 PV의 사용량을 확인하고 다음 명령을 실행하여 사용 가능한 공간이 충분한지 확인합니다.
$ oc debug <prometheus_k8s_pod_name> -n openshift-monitoring \1 --image=$(oc get po -n openshift-monitoring <prometheus_k8s_pod_name> \2 -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[?(@.name=="prometheus")].image}') -- df -h /prometheus/
다음 예제 출력에서는
prometheus-k8s-0Pod에서 클레임한 마운트된 PV가 남아 있는 공간의 63%를 보여줍니다.출력 예
Starting pod/prometheus-k8s-0-debug-j82w4 ... Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/nvme0n1p4 40G 15G 40G 37% /prometheus Removing debug pod ...
7.8. OpenShift CLI (oc) 문제 진단
7.8.1. OpenShift CLI (oc) 로그 수준 이해
OpenShift CLI(oc)를 사용하면 터미널에서 AWS 프로젝트에서 애플리케이션을 생성하고 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 관리할 수 있습니다.
oc 명령 관련 문제가 발생하면 oc 로그 수준을 높여서 명령으로 생성된 API 요청, API 응답 및 curl 요청 세부 정보를 출력합니다. 이를 통해 특정 oc 명령의 기본 작업에 대한 세부적인 보기를 통해 오류 특성에 대한 통찰력을 제공할 수 있습니다.
oc 로그 수준은 1에서 10까지 있습니다. 다음 표에서는 oc 로그 수준을 설명합니다.
표 7.3. OpenShift CLI (oc) 로그 수준
| 로그 수준 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 1~5 | stderr에 대한 추가 로깅이 없습니다. |
| 6 | stderr에 API 요청을 기록합니다. |
| 7 | stderr에 API 요청 및 헤더를 기록합니다. |
| 8 | stderr에 API 요청, 헤더 및 본문과 API 응답 헤더 및 본문을 기록합니다. |
| 9 |
stderr에 API 요청, 헤더 및 본문, API 응답 헤더 및 본문, |
| 10 |
stderr에 API 요청, 헤더 및 본문, API 응답 헤더 및 본문, |
7.8.2. OpenShift CLI (oc) 로그 수준 지정
명령의 로그 수준을 높여 OpenShift CLI (oc) 문제를 조사할 수 있습니다.
AWS 사용자의 현재 세션 토큰의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 일반적으로 필요한 경우 로깅된 curl 요청에 포함됩니다. oc 명령의 기본 프로세스 측면을 단계별로 테스트할 때 사용할 현재 사용자의 세션 토큰을 수동으로 가져올 수도 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
-
OpenShift CLI(
oc)를 설치합니다.
프로세스
oc명령을 실행할 때oc로그 레벨을 지정합니다.$ oc <command> --loglevel <log_level>
다음과 같습니다.
- <command>
- 실행 중인 명령을 지정합니다.
- <log_level>
- 명령에 적용할 로그 수준을 지정합니다.
현재 사용자의 세션 토큰을 얻으려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ oc whoami -t
출력 예
sha256~RCV3Qcn7H-OEfqCGVI0CvnZ6...
7.9. 만료된 토큰 문제 해결
7.9.1. 만료된 오프라인 액세스 토큰 문제 해결
AWS(ROSA) CLI, rosa 및 api.openshift.com 오프라인 액세스 토큰이 만료되면 오류 메시지가 표시됩니다. 이는 sso.redhat.com이 토큰을 무효화할 때 발생합니다.
출력 예
Can't get tokens .... Can't get access tokens ....
프로세스
다음 URL에서 새 오프라인 액세스 토큰을 생성합니다. URL을 방문할 때마다 새로운 오프라인 액세스 토큰이 생성됩니다.
- Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS(ROSA): https://console.redhat.com/openshift/token/rosa
7.10. IAM 역할 문제 해결
7.10.1. ocm-roles 및 user-role IAM 리소스 문제 해결
ROSA(Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS) CLI, rosa 를 사용하여 클러스터를 생성하려고 할 때 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
샘플 출력
E: Failed to create cluster: The sts_user_role is not linked to account '1oNl'. Please create a user role and link it to the account.
이 오류는 user-role IAM 역할이 AWS 계정에 연결되어 있지 않음을 의미합니다. 이 오류의 가장 큰 원인은 Red Hat 조직의 다른 사용자가 ocm-role IAM 역할을 생성했기 때문입니다. 사용자 역할 IAM 역할을 생성해야 합니다.
사용자가 Red Hat 계정에 연결된 ocm-role IAM 리소스를 설정한 후에는 Red Hat 조직에서 클러스터를 프로비저닝하기 위해 사용자 역할 IAM 역할이 있어야 합니다.
프로세스
다음 명령을 사용하여
ocm-role및user-roleIAM 역할의 상태를 평가합니다.$ rosa list ocm-role
샘플 출력
I: Fetching ocm roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ADMIN ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-1158 arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-1158 No No
$ rosa list user-role
샘플 출력
I: Fetching user roles ROLE NAME ROLE ARN LINKED ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role Yes
이러한 명령의 결과를 사용하여 누락된 IAM 리소스를 생성하고 연결할 수 있습니다.
7.10.1.1. ocm-role IAM 역할 생성
CLI(명령줄 인터페이스)를 사용하여 ocm-role IAM 역할을 생성합니다.
사전 요구 사항
- AWS 계정이 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 조직에 Red Hat 조직 관리자 권한이 있습니다.
- AWS 계정 전체 역할을 설치하는 데 필요한 권한이 있습니다.
-
설치 호스트에 최신 Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS(ROSA) CLI를 설치하고 구성했습니다.
프로세스
기본 권한으로 ocm-role IAM 역할을 생성하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ rosa create ocm-role
관리자 권한으로 ocm-role IAM 역할을 생성하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.
$ rosa create ocm-role --admin
이 명령을 사용하면 특정 속성을 지정하여 역할을 생성할 수 있습니다. 다음 예제 출력은 선택한 "자동 모드"를 표시하여 ROSA CLI(
rosa)에서 Operator 역할 및 정책을 생성할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 추가 리소스의 "계정 전체 역할 생성 방법"을 참조하십시오.
출력 예
I: Creating ocm role ? Role prefix: ManagedOpenShift 1 ? Enable admin capabilities for the OCM role (optional): No 2 ? Permissions boundary ARN (optional): 3 ? Role Path (optional): 4 ? Role creation mode: auto 5 I: Creating role using 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:user/<UserName>' ? Create the 'ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182' role? Yes 6 I: Created role 'ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182' with ARN 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182' I: Linking OCM role ? OCM Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182 7 ? Link the 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182' role with organization '<AWS ARN>'? Yes 8 I: Successfully linked role-arn 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-OCM-Role-182' with organization account '<AWS ARN>'
- 1
- 생성된 모든 AWS 리소스의 접두사 값입니다. 이 예제에서
Managed OpenShift는 모든 AWS 리소스 앞에 추가합니다. - 2
- 이 역할에 추가 관리자 권한이 있도록 하려면 선택합니다.참고
--admin옵션을 사용한 경우 이 프롬프트가 표시되지 않습니다. - 3
- 권한 경계를 설정하는 정책의 Amazon 리소스 이름(ARN)입니다.
- 4
- 사용자 이름에 대한 IAM 경로를 지정합니다.
- 5
- AWS 역할을 생성할 방법을 선택합니다. ROSA CLI는
auto를 사용하여 역할 및 정책을 생성하고 연결합니다.자동모드에서는 AWS 역할을 생성하라는 몇 가지 다른 프롬프트가 표시됩니다. - 6
auto메서드는 접두사를 사용하여 특정ocm-role을 생성할지 여부를 요청합니다.- 7
- IAM 역할을 OpenShift Cluster Manager와 연결할지 확인합니다.
- 8
- 생성된 역할을 AWS 조직과 연결합니다.
7.10.1.2. 사용자 역할 IAM 역할 생성
CLI(명령줄 인터페이스)를 사용하여 사용자 역할 IAM 역할을 생성할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- AWS 계정이 있습니다.
-
설치 호스트에 최신 Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS(ROSA) CLI를 설치하고 구성했습니다.
프로세스
기본 권한으로
사용자 역할IAM 역할을 생성하려면 다음 명령을 실행합니다.$ rosa create user-role
이 명령을 사용하면 특정 속성을 지정하여 역할을 생성할 수 있습니다. 다음 예제 출력은 선택한 "자동 모드"를 표시하여 ROSA CLI(
rosa)를 사용하여 Operator 역할 및 정책을 생성할 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 추가 리소스의 "자동 및 수동 배포 모드 이해"를 참조하십시오.
출력 예
I: Creating User role ? Role prefix: ManagedOpenShift 1 ? Permissions boundary ARN (optional): 2 ? Role Path (optional): 3 ? Role creation mode: auto 4 I: Creating ocm user role using 'arn:aws:iam::2066:user' ? Create the 'ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role' role? Yes 5 I: Created role 'ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role' with ARN 'arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role' I: Linking User role ? User Role ARN: arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role ? Link the 'arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role' role with account '1AGE'? Yes 6 I: Successfully linked role ARN 'arn:aws:iam::2066:role/ManagedOpenShift-User.osdocs-Role' with account '1AGE'
- 1
- 생성된 모든 AWS 리소스의 접두사 값입니다. 이 예제에서
Managed OpenShift는 모든 AWS 리소스 앞에 추가합니다. - 2
- 권한 경계를 설정하는 정책의 Amazon 리소스 이름(ARN)입니다.
- 3
- 사용자 이름에 대한 IAM 경로를 지정합니다.
- 4
- AWS 역할을 생성할 방법을 선택합니다. ROSA CLI는
auto를 사용하여 역할 및 정책을 생성하고 연결합니다.자동모드에서는 AWS 역할을 생성하라는 몇 가지 다른 프롬프트가 표시됩니다. - 5
auto메서드는 접두사를 사용하여 특정user-role을 생성할지 여부를 요청합니다.- 6
- 생성된 역할을 AWS 조직과 연결합니다.
7.10.1.3. AWS 계정 연결
ROSA(Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS) CLI, rosa 를 사용하여 AWS 계정을 기존 IAM 역할에 연결할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- AWS 계정이 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 를 사용하여 클러스터를 생성합니다.
- AWS 계정 전체 역할을 설치하는 데 필요한 권한이 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 이 섹션의 "추가 리소스"를 참조하십시오.
-
설치 호스트에 최신 AWS(
aws) 및 ROSA(rosa) CLI를 설치하고 구성했습니다. ocm-role및user-roleIAM 역할을 생성했지만 아직 AWS 계정에 연결되지 않았습니다. 다음 명령을 실행하여 IAM 역할이 이미 연결되어 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다.$ rosa list ocm-role
$ rosa list user-role
두 역할의
Linked열에Yes가 표시되면 이미 해당 역할을 AWS 계정에 연결했습니다.
프로세스
CLI에서 ARM(Amazon Resource Name)을 사용하여
ocm-role리소스를 Red Hat 조직에 연결합니다.참고rosa link명령을 실행하려면 Red Hat 조직 관리자 권한이 있어야 합니다.ocm-role리소스를 AWS 계정과 연결하면 조직의 모든 사용자에게 표시됩니다.$ rosa link ocm-role --role-arn <arn>
출력 예
I: Linking OCM role ? Link the '<AWS ACCOUNT ID>` role with organization '<ORG ID>'? Yes I: Successfully linked role-arn '<AWS ACCOUNT ID>' with organization account '<ORG ID>'
CLI에서 ARM(Amazon Resource Name)을 사용하여 사용자
역할리소스를 Red Hat 사용자 계정에 연결합니다.$ rosa link user-role --role-arn <arn>
출력 예
I: Linking User role ? Link the 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-Role-125' role with organization '<AWS ID>'? Yes I: Successfully linked role-arn 'arn:aws:iam::<ARN>:role/ManagedOpenShift-User-Role-125' with organization account '<AWS ID>'
7.10.1.4. 여러 AWS 계정을 Red Hat 조직과 연결
Red Hat 조직과 여러 AWS 계정을 연결할 수 있습니다. 여러 계정을 연결하면 Red Hat 조직의 관련 AWS 계정에서 AWS(ROSA)에서 Red Hat OpenShift Service를 생성할 수 있습니다.
이 기능을 사용하면 여러 AWS 프로필을 지역 바인딩 환경으로 사용하여 다른 AWS 리전에서 클러스터를 생성할 수 있습니다.
사전 요구 사항
- AWS 계정이 있습니다.
- OpenShift Cluster Manager 를 사용하여 클러스터를 생성합니다.
- AWS 계정 전체 역할을 설치하는 데 필요한 권한이 있습니다.
-
설치 호스트에 최신 AWS(
aws) 및 ROSA(rosa) CLI를 설치하고 구성했습니다. -
ocm-role및user-roleIAM 역할을 생성했습니다.
프로세스
추가 AWS 계정을 연결하려면 먼저 로컬 AWS 구성에 프로필을 생성합니다. 그런 다음 추가 AWS 계정에서 ocm-role, user 및 account 역할을 생성하여 계정을 Red Hat 조직과 연결합니다.
추가 리전에서 역할을 생성하려면 > 매개변수를 지정하고 < rosa create 명령을 실행할 때 --profile <aws-profileaws_profile >을 추가 계정 프로필 이름으로 교체합니다.
OpenShift Cluster Manager 역할을 생성할 때 AWS 계정 프로필을 지정하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
$ rosa create --profile <aws_profile> ocm-role
사용자 역할을 생성할 때 AWS 계정 프로필을 지정하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
$ rosa create --profile <aws_profile> user-role
계정 역할을 생성할 때 AWS 계정 프로필을 지정하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
$ rosa create --profile <aws_profile> account-roles
프로필을 지정하지 않으면 기본 AWS 프로필이 사용됩니다.
7.11. 클러스터 배포 문제 해결
이 문서에서는 클러스터 배포 오류 문제를 해결하는 방법을 설명합니다.
7.11.1. 실패한 클러스터에 대한 정보 얻기
클러스터 배포에 실패하면 클러스터가 "오류" 상태가 됩니다.
프로세스
다음 명령을 실행하여 자세한 정보를 가져옵니다.
$ rosa describe cluster -c <my_cluster_name> --debug
7.11.2. osdCcsAdmin 오류가 있는 클러스터를 생성하지 못했습니다
클러스터 생성 작업에 실패하면 다음과 같은 오류 메시지가 표시될 수 있습니다.
출력 예
Failed to create cluster: Unable to create cluster spec: Failed to get access keys for user 'osdCcsAdmin': NoSuchEntity: The user with name osdCcsAdmin cannot be found.
프로세스
이 문제를 해결하려면 다음을 수행합니다.
스택을 삭제합니다.
$ rosa init --delete
계정을 다시 초기화합니다.
$ rosa init
7.11.3. ELB(Elastic Load Balancing) 서비스 연결 역할 생성
AWS 계정에서 로드 밸런서를 생성하지 않은 경우 ELB(Elastic Load Balancing)의 서비스 연결 역할이 아직 존재하지 않을 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
Error: Error creating network Load Balancer: AccessDenied: User: arn:aws:sts::xxxxxxxxxxxx:assumed-role/ManagedOpenShift-Installer-Role/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx is not authorized to perform: iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole on resource: arn:aws:iam::xxxxxxxxxxxx:role/aws-service-role/elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing"
프로세스
이 문제를 해결하려면 역할이 AWS 계정에 있는지 확인합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 다음 명령을 사용하여 이 역할을 생성합니다.
aws iam get-role --role-name "AWSServiceRoleForElasticLoadBalancing" || aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name "elasticloadbalancing.amazonaws.com"
이 명령은 계정당 한 번만 실행해야 합니다.
7.11.4. 삭제할 수 없는 클러스터 복구
특정 경우에는 클러스터를 삭제하려고 하면 OpenShift Cluster Manager 에 다음 오류가 표시됩니다.
Error deleting cluster CLUSTERS-MGMT-400: Failed to delete cluster <hash>: sts_user_role is not linked to your account. sts_ocm_role is linked to your organization <org number> which requires sts_user_role to be linked to your Red Hat account <account ID>.Please create a user role and link it to the account: User Account <account ID> is not authorized to perform STS cluster operations Operation ID: b0572d6e-fe54-499b-8c97-46bf6890011c
CLI에서 클러스터를 삭제하려고 하면 다음 오류가 표시됩니다.
E: Failed to delete cluster <hash>: sts_user_role is not linked to your account. sts_ocm_role is linked to your organization <org_number> which requires sts_user_role to be linked to your Red Hat account <account_id>.Please create a user role and link it to the account: User Account <account ID> is not authorized to perform STS cluster operations
이 오류는 user-role 이 연결 해제되거나 삭제될 때 발생합니다.
프로세스
다음 명령을 실행하여
user-roleIAM 리소스를 생성합니다.$ rosa create user-role
역할이 생성된 것을 확인한 후 클러스터를 삭제할 수 있습니다. 다음은 역할이 생성되고 연결되어 있음을 확인합니다.
I: Successfully linked role ARN <user role ARN> with account <account ID>
7.12. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS 관리 리소스
7.12.1. 개요
다음은 SRE-P(Service Reliability Engineering Platform) 팀에서 관리하거나 보호하는 모든 리소스에 대해 다룹니다. 이로 인해 클러스터 불안정성이 발생할 수 있으므로 고객은 이러한 리소스를 수정하려고 시도하지 않아야 합니다.
7.12.2. Hive 관리형 리소스
다음 목록에는 중앙 집중식 플릿 구성 관리 시스템인 OpenShift Hive에서 관리하는 AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service가 표시되어 있습니다. 이러한 리소스는 설치 중에 생성된 OpenShift Container Platform 리소스 외에도 제공됩니다. OpenShift Hive는 AWS 클러스터의 모든 Red Hat OpenShift Service에서 일관성을 지속적으로 유지하려고 합니다. AWS 리소스의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 OpenShift Cluster Manager 및 Hive가 동기화되도록 OpenShift Cluster Manager를 통해 변경해야 합니다. OpenShift Cluster Manager에서 해당 리소스 수정을 지원하지 않는 경우 ocm-feedback@redhat.com 에 문의하십시오.
예 7.1. Hive 관리 리소스 목록
Resources:
ConfigMap:
- namespace: openshift-config
name: rosa-brand-logo
- namespace: openshift-console
name: custom-logo
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-config
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: fr-aide-conf
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator-config
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: cluster-monitoring-config
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: managed-namespaces
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: ocp-namespaces
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter-code
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter-trusted-ca-bundle
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-code
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-trusted-ca-bundle
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-code
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-trusted-ca-bundle
- namespace: openshift-security
name: osd-audit-policy
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: webhook-cert
- namespace: openshift
name: motd
Endpoints:
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-metrics
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: loggerservice
- namespace: openshift-security
name: audit-exporter
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: validation-webhook
Namespace:
- name: dedicated-admin
- name: openshift-addon-operator
- name: openshift-aqua
- name: openshift-aws-vpce-operator
- name: openshift-backplane
- name: openshift-backplane-cee
- name: openshift-backplane-csa
- name: openshift-backplane-cse
- name: openshift-backplane-csm
- name: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
- name: openshift-backplane-mobb
- name: openshift-backplane-srep
- name: openshift-backplane-tam
- name: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
- name: openshift-codeready-workspaces
- name: openshift-compliance
- name: openshift-compliance-monkey
- name: openshift-container-security
- name: openshift-custom-domains-operator
- name: openshift-customer-monitoring
- name: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
- name: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
- name: openshift-file-integrity
- name: openshift-logging
- name: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
- name: openshift-must-gather-operator
- name: openshift-observability-operator
- name: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
- name: openshift-operators-redhat
- name: openshift-osd-metrics
- name: openshift-rbac-permissions
- name: openshift-route-monitor-operator
- name: openshift-scanning
- name: openshift-security
- name: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
- name: openshift-sre-pruning
- name: openshift-suricata
- name: openshift-validation-webhook
- name: openshift-velero
- name: openshift-monitoring
- name: openshift
- name: openshift-cluster-version
- name: keycloak
- name: goalert
- name: configure-goalert-operator
ReplicationController:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-1
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-1
Secret:
- namespace: openshift-authentication
name: v4-0-config-user-idp-0-file-data
- namespace: openshift-authentication
name: v4-0-config-user-template-error
- namespace: openshift-authentication
name: v4-0-config-user-template-login
- namespace: openshift-authentication
name: v4-0-config-user-template-provider-selection
- namespace: openshift-config
name: htpasswd-secret
- namespace: openshift-config
name: osd-oauth-templates-errors
- namespace: openshift-config
name: osd-oauth-templates-login
- namespace: openshift-config
name: osd-oauth-templates-providers
- namespace: openshift-config
name: rosa-oauth-templates-errors
- namespace: openshift-config
name: rosa-oauth-templates-login
- namespace: openshift-config
name: rosa-oauth-templates-providers
- namespace: openshift-config
name: support
- namespace: openshift-config
name: tony-devlab-primary-cert-bundle-secret
- namespace: openshift-ingress
name: tony-devlab-primary-cert-bundle-secret
- namespace: openshift-kube-apiserver
name: user-serving-cert-000
- namespace: openshift-kube-apiserver
name: user-serving-cert-001
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: dms-secret
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: observatorium-credentials
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: pd-secret
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: clam-secrets
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: logger-secrets
- namespace: openshift-security
name: splunk-auth
ServiceAccount:
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: osd-backplane
- namespace: openshift-backplane-srep
name: 6804d07fb268b8285b023bcf65392f0e
- namespace: openshift-backplane-srep
name: osd-delete-ownerrefs-serviceaccounts
- namespace: openshift-backplane
name: osd-delete-backplane-serviceaccounts
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: custom-domains-operator
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-disable-cpms
- namespace: openshift-marketplace
name: osd-patch-subscription-source
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: configure-alertmanager-operator
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
- namespace: openshift-network-diagnostics
name: sre-pod-network-connectivity-check-pruner
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocm-agent-operator
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: splunk-forwarder-operator
- namespace: openshift-sre-pruning
name: bz1980755
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: logger-sa
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: scanner-sa
- namespace: openshift-sre-pruning
name: sre-pruner-sa
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: ids-test
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: suricata-sa
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: validation-webhook
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: velero
- namespace: openshift-backplane-srep
name: UNIQUE_BACKPLANE_SERVICEACCOUNT_ID
Service:
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-metrics
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: loggerservice
- namespace: openshift-security
name: audit-exporter
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: validation-webhook
AddonOperator:
- name: addon-operator
ValidatingWebhookConfiguration:
- name: sre-hiveownership-validation
- name: sre-namespace-validation
- name: sre-pod-validation
- name: sre-prometheusrule-validation
- name: sre-regular-user-validation
- name: sre-scc-validation
- name: sre-techpreviewnoupgrade-validation
DaemonSet:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: logger
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: scanner
- namespace: openshift-security
name: audit-exporter
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: suricata
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: validation-webhook
DeploymentConfig:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
ClusterRoleBinding:
- name: aqua-scanner-binding
- name: backplane-cluster-admin
- name: backplane-impersonate-cluster-admin
- name: bz1980755
- name: configure-alertmanager-operator-prom
- name: dedicated-admins-cluster
- name: dedicated-admins-registry-cas-cluster
- name: logger-clusterrolebinding
- name: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts-reader
- name: osd-cluster-admin
- name: osd-cluster-ready
- name: osd-delete-backplane-script-resources
- name: osd-delete-ownerrefs-serviceaccounts
- name: osd-patch-subscription-source
- name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes
- name: pcap-dedicated-admins
- name: splunk-forwarder-operator
- name: splunk-forwarder-operator-clusterrolebinding
- name: sre-pod-network-connectivity-check-pruner
- name: sre-pruner-buildsdeploys-pruning
- name: velero
- name: webhook-validation
ClusterRole:
- name: backplane-cee-readers-cluster
- name: backplane-impersonate-cluster-admin
- name: backplane-readers-cluster
- name: backplane-srep-admins-cluster
- name: backplane-srep-admins-project
- name: bz1980755
- name: dedicated-admins-aggregate-cluster
- name: dedicated-admins-aggregate-project
- name: dedicated-admins-cluster
- name: dedicated-admins-manage-operators
- name: dedicated-admins-project
- name: dedicated-admins-registry-cas-cluster
- name: dedicated-readers
- name: image-scanner
- name: logger-clusterrole
- name: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts-reader
- name: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
- name: osd-cluster-ready
- name: osd-custom-domains-dedicated-admin-cluster
- name: osd-delete-backplane-script-resources
- name: osd-delete-backplane-serviceaccounts
- name: osd-delete-ownerrefs-serviceaccounts
- name: osd-get-namespace
- name: osd-netnamespaces-dedicated-admin-cluster
- name: osd-patch-subscription-source
- name: osd-readers-aggregate
- name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes
- name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- name: pcap-dedicated-admins
- name: splunk-forwarder-operator
- name: sre-allow-read-machine-info
- name: sre-pruner-buildsdeploys-cr
- name: webhook-validation-cr
RoleBinding:
- namespace: kube-system
name: cloud-ingress-operator-cluster-config-v1-reader
- namespace: kube-system
name: managed-velero-operator-cluster-config-v1-reader
- namespace: openshift-aqua
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-aqua
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: backplane-cee-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: backplane-srep-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: osd-delete-backplane-script-resources
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-codeready-workspaces
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-codeready-workspaces
- namespace: openshift-config
name: dedicated-admins-project-request
- namespace: openshift-config
name: dedicated-admins-registry-cas-project
- namespace: openshift-config
name: muo-pullsecret-reader
- namespace: openshift-config
name: oao-openshiftconfig-reader
- namespace: openshift-config
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-customer-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-customer-monitoring
name: prometheus-k8s-openshift-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-dns
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-dns
- namespace: openshift-dns
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-dns
- namespace: openshift-image-registry
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-ingress
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-kube-apiserver
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: admin-dedicated-admins
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: admin-system:serviceaccounts:dedicated-admin
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: openshift-logging-dedicated-admins
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: openshift-logging:serviceaccounts:dedicated-admin
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-read-machine-info
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-read-machine-info
- namespace: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-disable-cpms
- namespace: openshift-marketplace
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-marketplace
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: backplane-cee
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: muo-monitoring-reader
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: oao-monitoring-manager
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: backplane-cee-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: backplane-srep-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-network-diagnostics
name: sre-pod-network-connectivity-check-pruner
- namespace: openshift-network-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-operators-redhat
name: admin-dedicated-admins
- namespace: openshift-operators-redhat
name: admin-system:serviceaccounts:dedicated-admin
- namespace: openshift-operators-redhat
name: openshift-operators-redhat-dedicated-admins
- namespace: openshift-operators-redhat
name: openshift-operators-redhat:serviceaccounts:dedicated-admin
- namespace: openshift-operators
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-operators
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: scanner-rolebinding
- namespace: openshift-security
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-security
- namespace: openshift-security
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: suricata-rolebinding
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-uwm-config-create
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-uwm-config-edit
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-uwm-managed-am-secret
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-user-workload-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-pod-rebalance
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: prometheus-k8s
Role:
- namespace: kube-system
name: cluster-config-v1-reader
- namespace: kube-system
name: cluster-config-v1-reader-cio
- namespace: openshift-aqua
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-aqua
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: backplane-cee-pcap-collector
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: backplane-srep-pcap-collector
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: osd-delete-backplane-script-resources
- namespace: openshift-codeready-workspaces
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-codeready-workspaces
- namespace: openshift-config
name: dedicated-admins-project-request
- namespace: openshift-config
name: dedicated-admins-registry-cas-project
- namespace: openshift-config
name: muo-pullsecret-reader
- namespace: openshift-config
name: oao-openshiftconfig-reader
- namespace: openshift-config
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-customer-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-customer-monitoring
name: prometheus-k8s-openshift-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-dns
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-dns
- namespace: openshift-dns
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-dns
- namespace: openshift-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-ingress
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-kube-apiserver
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-logging
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-disable-cpms
- namespace: openshift-marketplace
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-marketplace
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: backplane-cee
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: muo-monitoring-reader
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: oao-monitoring-manager
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-cluster-ready
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: backplane-cee-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: backplane-srep-mustgather
- namespace: openshift-network-diagnostics
name: sre-pod-network-connectivity-check-pruner
- namespace: openshift-operators
name: dedicated-admins-openshift-operators
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: scanner-role
- namespace: openshift-security
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-security
- namespace: openshift-security
name: prometheus-k8s
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: suricata-role
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-user-workload-monitoring-create-cm
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: dedicated-admins-user-workload-monitoring-manage-am-secret
- namespace: openshift-user-workload-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes-openshift-user-workload-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: prometheus-k8s
CronJob:
- namespace: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
name: osd-delete-backplane-script-resources
- namespace: openshift-backplane-srep
name: osd-delete-ownerrefs-serviceaccounts
- namespace: openshift-backplane
name: osd-delete-backplane-serviceaccounts
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: osd-disable-cpms
- namespace: openshift-marketplace
name: osd-patch-subscription-source
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-rebalance-infra-nodes
- namespace: openshift-network-diagnostics
name: sre-pod-network-connectivity-check-pruner
- namespace: openshift-sre-pruning
name: builds-pruner
- namespace: openshift-sre-pruning
name: bz1980755
- namespace: openshift-sre-pruning
name: deployments-pruner
- namespace: openshift-suricata
name: ids-tester
Job:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: osd-cluster-ready
CredentialsRequest:
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator-credentials-aws
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator-credentials-gcp
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-aws-credentials
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-aws-credentials
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator-iam-credentials-aws
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator-iam-credentials-gcp
APIScheme:
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: rh-api
PublishingStrategy:
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: publishingstrategy
ScanSettingBinding:
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: fedramp-high-ocp
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: fedramp-high-rhcos
ScanSetting:
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: osd
TailoredProfile:
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: rhcos4-high-rosa
OAuth:
- name: cluster
EndpointSlice:
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-metrics-rhtwg
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter-4cw9r
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter-6tx5g
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols-gmdhs
- namespace: openshift-scanning
name: loggerservice-zprbq
- namespace: openshift-security
name: audit-exporter-nqfdk
- namespace: openshift-validation-webhook
name: validation-webhook-97b8t
FileIntegrity:
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: osd-fileintegrity
MachineHealthCheck:
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: srep-infra-healthcheck
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: srep-metal-worker-healthcheck
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: srep-worker-healthcheck
MachineSet:
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: sbasabat-mc-qhqkn-infra-us-east-1a
- namespace: openshift-machine-api
name: sbasabat-mc-qhqkn-worker-us-east-1a
ContainerRuntimeConfig:
- name: custom-crio
KubeletConfig:
- name: custom-kubelet
MachineConfig:
- name: 00-master-chrony
- name: 00-worker-chrony
SubjectPermission:
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-cee
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-csa
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-cse
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-csm
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-mobb
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-srep
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: backplane-tam
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admin-serviceaccounts
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admin-serviceaccounts-core-ns
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admins
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admins-alert-routing-edit
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admins-core-ns
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: dedicated-admins-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: osd-delete-backplane-serviceaccounts
VeleroInstall:
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: cluster
PrometheusRule:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: rhmi-sre-cluster-admins
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: rhoam-sre-cluster-admins
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-alertmanager-silences-active
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-alerts-stuck-builds
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-alerts-stuck-volumes
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-cloud-ingress-operator-offline-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-avo-pendingacceptance
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-configure-alertmanager-operator-offline-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-control-plane-resizing-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-burstbalance
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-elasticsearch-jobs
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-elasticsearch-managed-notification-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-excessive-memory
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-fr-alerts-low-disk-space
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-haproxy-reload-fail
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-internal-slo-recording-rules
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-kubequotaexceeded
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-leader-election-master-status-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-kube-apiserver-missing-on-node
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-kube-controller-manager-missing-on-node
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-kube-scheduler-missing-on-node
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-node-metadata-operator-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-notification-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-upgrade-operator-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-managed-velero-operator-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-node-unschedulable
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-oauth-server
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-pending-csr-alert
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-proxy-managed-notification-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-pruning
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-pv
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-router-health
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-runaway-sdn-preventing-container-creation
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-slo-recording-rules
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-telemeter-client
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-telemetry-managed-labels-recording-rules
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-upgrade-send-managed-notification-alerts
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-uptime-sla
ServiceMonitor:
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-dns-latency-exporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-ebs-iops-reporter
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: sre-stuck-ebs-vols
ClusterUrlMonitor:
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: api
RouteMonitor:
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: console
NetworkPolicy:
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: allow-from-openshift-insights
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: allow-from-openshift-olm
ManagedNotification:
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: sre-elasticsearch-managed-notifications
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: sre-managed-notifications
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: sre-proxy-managed-notifications
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: sre-upgrade-managed-notifications
OcmAgent:
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocmagent
- namespace: openshift-security
name: audit-exporter
Console:
- name: cluster
CatalogSource:
- namespace: openshift-addon-operator
name: addon-operator-catalog
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: compliance-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-container-security
name: container-security-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: custom-domains-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-catalog
- namespace: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
name: managed-node-metadata-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: file-integrity-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator-catalog
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: configure-alertmanager-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: must-gather-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-observability-operator
name: observability-operator-catalog
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocm-agent-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: osd-metrics-exporter-registry
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: route-monitor-operator-registry
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: splunk-forwarder-operator-catalog
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator-registry
OperatorGroup:
- namespace: openshift-addon-operator
name: addon-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-aqua
name: openshift-aqua
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-codeready-workspaces
name: openshift-codeready-workspaces
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: compliance-operator
- namespace: openshift-container-security
name: container-security-operator
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: custom-domains-operator
- namespace: openshift-customer-monitoring
name: openshift-customer-monitoring
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
name: managed-node-metadata-operator
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: file-integrity-operator
- namespace: openshift-logging
name: openshift-logging
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: must-gather-operator
- namespace: openshift-observability-operator
name: observability-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocm-agent-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: osd-metrics-exporter
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: route-monitor-operator
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: splunk-forwarder-operator-og
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator
Subscription:
- namespace: openshift-addon-operator
name: addon-operator
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: compliance-operator-sub
- namespace: openshift-container-security
name: container-security-operator-sub
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: custom-domains-operator
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator
- namespace: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
name: managed-node-metadata-operator
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: file-integrity-operator-sub
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: configure-alertmanager-operator
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: must-gather-operator
- namespace: openshift-observability-operator
name: observability-operator
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocm-agent-operator
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: osd-metrics-exporter
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: route-monitor-operator
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator
PackageManifest:
- namespace: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
name: splunk-forwarder-operator
- namespace: openshift-addon-operator
name: addon-operator
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator
- namespace: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
name: cloud-ingress-operator
- namespace: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
name: managed-node-metadata-operator
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: managed-velero-operator
- namespace: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator
- namespace: openshift-container-security
name: container-security-operator
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: route-monitor-operator
- namespace: openshift-file-integrity
name: file-integrity-operator
- namespace: openshift-custom-domains-operator
name: managed-node-metadata-operator
- namespace: openshift-route-monitor-operator
name: custom-domains-operator
- namespace: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
name: managed-upgrade-operator
- namespace: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
name: ocm-agent-operator
- namespace: openshift-observability-operator
name: observability-operator
- namespace: openshift-monitoring
name: configure-alertmanager-operator
- namespace: openshift-must-gather-operator
name: deployment-validation-operator
- namespace: openshift-osd-metrics
name: osd-metrics-exporter
- namespace: openshift-compliance
name: compliance-operator
- namespace: openshift-rbac-permissions
name: rbac-permissions-operator
Status:
- {}
Project:
- name: dedicated-admin
- name: openshift-addon-operator
- name: openshift-aqua
- name: openshift-backplane
- name: openshift-backplane-cee
- name: openshift-backplane-csa
- name: openshift-backplane-cse
- name: openshift-backplane-csm
- name: openshift-backplane-managed-scripts
- name: openshift-backplane-mobb
- name: openshift-backplane-srep
- name: openshift-backplane-tam
- name: openshift-cloud-ingress-operator
- name: openshift-codeready-workspaces
- name: openshift-compliance
- name: openshift-container-security
- name: openshift-custom-domains-operator
- name: openshift-customer-monitoring
- name: openshift-deployment-validation-operator
- name: openshift-managed-node-metadata-operator
- name: openshift-file-integrity
- name: openshift-logging
- name: openshift-managed-upgrade-operator
- name: openshift-must-gather-operator
- name: openshift-observability-operator
- name: openshift-ocm-agent-operator
- name: openshift-operators-redhat
- name: openshift-osd-metrics
- name: openshift-rbac-permissions
- name: openshift-route-monitor-operator
- name: openshift-scanning
- name: openshift-security
- name: openshift-splunk-forwarder-operator
- name: openshift-sre-pruning
- name: openshift-suricata
- name: openshift-validation-webhook
- name: openshift-velero
ClusterResourceQuota:
- name: loadbalancer-quota
- name: persistent-volume-quota
SecurityContextConstraints:
- name: osd-scanning-scc
- name: osd-suricata-scc
- name: pcap-dedicated-admins
- name: splunkforwarder
SplunkForwarder:
- namespace: openshift-security
name: splunkforwarder
Group:
- name: cluster-admins
- name: dedicated-admins
User:
- name: backplane-cluster-admin
Backup:
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221123112305
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221125042537
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221126010038
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221127010039
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221128010040
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup-20221129050847
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221128051740
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221128061740
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221128071740
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221128081740
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221128091740
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221129050852
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup-20221129051747
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: weekly-full-backup-20221116184315
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: weekly-full-backup-20221121033854
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: weekly-full-backup-20221128020040
Schedule:
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: daily-full-backup
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: hourly-object-backup
- namespace: openshift-velero
name: weekly-full-backup7.12.3. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS 애드온 네임스페이스
AWS 애드온의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 클러스터 설치 후 설치에 사용할 수 있는 서비스입니다. 이러한 추가 서비스에는 Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces, Red Hat OpenShift API Management 및 Cluster Logging Operator가 포함됩니다. 다음 네임스페이스 내의 리소스에 대한 모든 변경 사항은 업그레이드 중에 애드온으로 재정의할 수 있으므로 추가 기능에 대해 지원되지 않는 구성이 발생할 수 있습니다.
예 7.2. 애드온 관리 네임스페이스 목록
addon-namespaces: ocs-converged-dev: openshift-storage managed-api-service-internal: redhat-rhoami-operator codeready-workspaces-operator: codeready-workspaces-operator managed-odh: redhat-ods-operator codeready-workspaces-operator-qe: codeready-workspaces-operator-qe integreatly-operator: redhat-rhmi-operator nvidia-gpu-addon: redhat-nvidia-gpu-addon integreatly-operator-internal: redhat-rhmi-operator rhoams: redhat-rhoam-operator ocs-converged: openshift-storage addon-operator: redhat-addon-operator prow-operator: prow cluster-logging-operator: openshift-logging advanced-cluster-management: redhat-open-cluster-management cert-manager-operator: redhat-cert-manager-operator dba-operator: addon-dba-operator reference-addon: redhat-reference-addon ocm-addon-test-operator: redhat-ocm-addon-test-operator
7.12.4. AWS의 Red Hat OpenShift Service 검증 Webhook
AWS 검증 웹 후크의 Red Hat OpenShift Service는 OpenShift SRE 팀에서 유지 관리하는 동적 승인 제어 집합입니다. 클러스터의 안정성을 보장하기 위해 다양한 유형의 요청에 대해 Webhook라고도 하는 이러한 HTTP 콜백이 호출됩니다. 다음 목록에서는 제어되는 등록된 작업 및 리소스가 포함된 규칙이 포함된 다양한 Webhook에 대해 설명합니다. 이러한 검증 웹 후크를 우회하려고 하면 클러스터의 안정성 및 지원 가능성에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
예 7.3. 검증 Webhook 목록
[
{
"webhookName": "clusterlogging-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"logging.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"v1"
],
"resources": [
"clusterloggings"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may set log retention outside the allowed range of 0-7 days"
},
{
"webhookName": "clusterrolebindings-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"v1"
],
"resources": [
"clusterrolebindings"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not delete the cluster role bindings under the managed namespaces: (^openshift-.*|kube-system)"
},
{
"webhookName": "customresourcedefinitions-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"apiextensions.k8s.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"customresourcedefinitions"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not change CustomResourceDefinitions managed by Red Hat."
},
{
"webhookName": "hiveownership-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"quota.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"clusterresourcequotas"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"webhookObjectSelector": {
"matchLabels": {
"hive.openshift.io/managed": "true"
}
},
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not edit certain managed resources. A managed resource has a \"hive.openshift.io/managed\": \"true\" label."
},
{
"webhookName": "imagecontentpolicies-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"config.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"imagedigestmirrorsets",
"imagetagmirrorsets"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
},
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"operator.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"imagecontentsourcepolicies"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not create ImageContentSourcePolicy, ImageDigestMirrorSet, or ImageTagMirrorSet resources that configure mirrors that would conflict with system registries (e.g. quay.io, registry.redhat.io, registry.access.redhat.com, etc). For more details, see https://docs.openshift.com/"
},
{
"webhookName": "ingress-config-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"config.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"ingresses"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not modify ingress config resources because it can can degrade cluster operators and can interfere with OpenShift SRE monitoring."
},
{
"webhookName": "ingresscontroller-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"operator.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"ingresscontroller",
"ingresscontrollers"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customer may create IngressControllers without necessary taints. This can cause those workloads to be provisioned on infra or master nodes."
},
{
"webhookName": "namespace-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
""
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"namespaces"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not modify namespaces specified in the [openshift-monitoring/managed-namespaces openshift-monitoring/ocp-namespaces] ConfigMaps because customer workloads should be placed in customer-created namespaces. Customers may not create namespaces identified by this regular expression (^com$|^io$|^in$) because it could interfere with critical DNS resolution. Additionally, customers may not set or change the values of these Namespace labels [managed.openshift.io/storage-pv-quota-exempt managed.openshift.io/service-lb-quota-exempt]."
},
{
"webhookName": "networkpolicies-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"networking.k8s.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"networkpolicies"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not create NetworkPolicies in namespaces managed by Red Hat."
},
{
"webhookName": "node-validation-osd",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
""
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"nodes",
"nodes/*"
],
"scope": "*"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not alter Node objects."
},
{
"webhookName": "pod-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"v1"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"pods"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may use tolerations on Pods that could cause those Pods to be scheduled on infra or master nodes."
},
{
"webhookName": "prometheusrule-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"monitoring.coreos.com"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"prometheusrules"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not create PrometheusRule in namespaces managed by Red Hat."
},
{
"webhookName": "regular-user-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"cloudcredential.openshift.io",
"machine.openshift.io",
"admissionregistration.k8s.io",
"addons.managed.openshift.io",
"cloudingress.managed.openshift.io",
"managed.openshift.io",
"ocmagent.managed.openshift.io",
"splunkforwarder.managed.openshift.io",
"upgrade.managed.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"*/*"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"autoscaling.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"clusterautoscalers",
"machineautoscalers"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"config.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"clusterversions",
"clusterversions/status",
"schedulers",
"apiservers",
"proxies"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
""
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"configmaps"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"machineconfiguration.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"machineconfigs",
"machineconfigpools"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"operator.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"kubeapiservers",
"openshiftapiservers"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"managed.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"subjectpermissions",
"subjectpermissions/*"
],
"scope": "*"
},
{
"operations": [
"*"
],
"apiGroups": [
"network.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"netnamespaces",
"netnamespaces/*"
],
"scope": "*"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not manage any objects in the following APIGroups [autoscaling.openshift.io network.openshift.io machine.openshift.io admissionregistration.k8s.io addons.managed.openshift.io cloudingress.managed.openshift.io splunkforwarder.managed.openshift.io upgrade.managed.openshift.io managed.openshift.io ocmagent.managed.openshift.io config.openshift.io machineconfiguration.openshift.io operator.openshift.io cloudcredential.openshift.io], nor may Managed OpenShift customers alter the APIServer, KubeAPIServer, OpenShiftAPIServer, ClusterVersion, Proxy or SubjectPermission objects."
},
{
"webhookName": "scc-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"UPDATE",
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"security.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"securitycontextconstraints"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not modify the following default SCCs: [anyuid hostaccess hostmount-anyuid hostnetwork hostnetwork-v2 node-exporter nonroot nonroot-v2 privileged restricted restricted-v2]"
},
{
"webhookName": "sdn-migration-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"config.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"networks"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift customers may not modify the network config type because it can can degrade cluster operators and can interfere with OpenShift SRE monitoring."
},
{
"webhookName": "service-mutation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
""
],
"apiVersions": [
"v1"
],
"resources": [
"services"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "LoadBalancer-type services on Managed OpenShift clusters must contain an additional annotation for managed policy compliance."
},
{
"webhookName": "serviceaccount-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"DELETE"
],
"apiGroups": [
""
],
"apiVersions": [
"v1"
],
"resources": [
"serviceaccounts"
],
"scope": "Namespaced"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not delete the service accounts under the managed namespaces。"
},
{
"webhookName": "techpreviewnoupgrade-validation",
"rules": [
{
"operations": [
"CREATE",
"UPDATE"
],
"apiGroups": [
"config.openshift.io"
],
"apiVersions": [
"*"
],
"resources": [
"featuregates"
],
"scope": "Cluster"
}
],
"documentString": "Managed OpenShift Customers may not use TechPreviewNoUpgrade FeatureGate that could prevent any future ability to do a y-stream upgrade to their clusters."
}
]
